Traditional gene mapping has been applied successfully to a variety of organisms including yeast, fungi, maize, and Drosophila. However, human gene mapping has only recently shared a similar spotlight. What factors have delayed the application of traditional gene-mapping techniques in humans?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 28b
Textbook Question
Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder inherited on human chromosome 17. Part of the analysis mapping the NF1 gene to chromosome 17 came from genetic linkage studies testing segregation of NF1 and DNA genetic markers on various chromosomes. A DNA marker with two alleles, designated 1 and 2, is linked to NF1. The pedigree below shows segregation of NF1 (darkened symbols) and gives genotypes for the DNA marker for each family member.
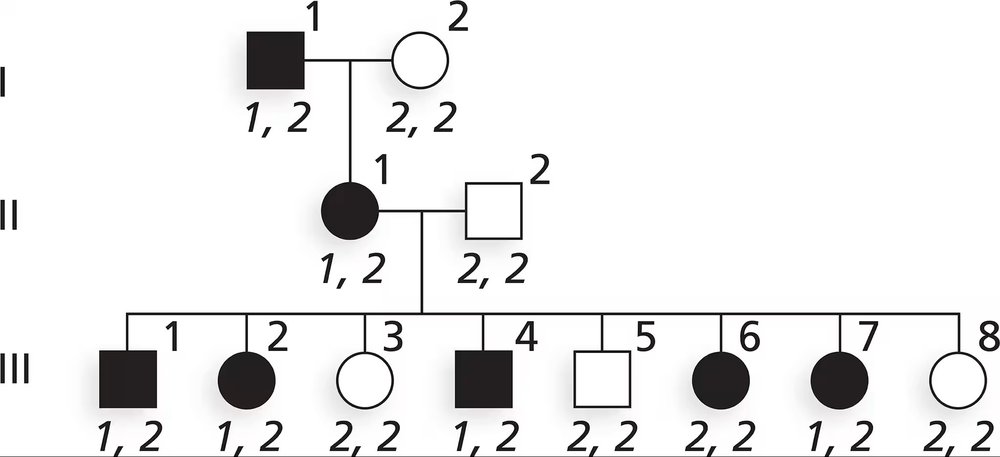
Based on the phase of alleles on chromosomes in generation II, is there any evidence of recombination among the eight offspring in generation III? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the problem. Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder linked to a DNA marker with two alleles (1 and 2). The goal is to determine if recombination occurred among the eight offspring in generation III based on the phase of alleles in generation II.
Step 2: Define key concepts. Recombination refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which can result in new combinations of alleles. The 'phase' of alleles refers to the arrangement of alleles on the parental chromosomes.
Step 3: Analyze the pedigree. Examine the genotypes of generation II individuals to determine the phase of alleles (which allele is linked to NF1 on the same chromosome). This involves identifying which allele (1 or 2) is consistently inherited with NF1 in generation II.
Step 4: Compare the genotypes of generation III offspring. Check if any offspring have inherited a combination of alleles that differs from the parental phase established in generation II. If such combinations exist, it indicates recombination.
Step 5: Summarize findings. Based on the comparison, determine whether evidence of recombination is present among the eight offspring in generation III. Provide reasoning based on the observed inheritance patterns and linkage of alleles.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to a pattern where only one copy of a mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in offspring. This means that if a parent has the disorder, there is a 50% chance for each child to inherit the condition. Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) exemplifies this inheritance pattern, as it is caused by mutations in a gene located on an autosome, specifically chromosome 17.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Genetic Linkage and Markers
Genetic linkage occurs when genes are located close to each other on a chromosome and tend to be inherited together. DNA markers, which are specific sequences of DNA with known locations, can be used to track the inheritance of traits. In the context of NF1, the presence of a DNA marker with two alleles linked to the NF1 gene helps researchers determine the inheritance patterns and potential recombination events during meiosis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers
Recombination
Recombination is the process during meiosis where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, leading to new allele combinations in offspring. This can affect the inheritance of linked genes, such as the NF1 gene and its associated DNA markers. By analyzing the genotypes of offspring in generation III, one can determine if recombination has occurred by observing whether the offspring exhibit combinations of alleles that differ from those of their parents.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Recombination after Single Strand Breaks
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
464
views


