Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 28c
Textbook Question
Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder inherited on human chromosome 17. Part of the analysis mapping the NF1 gene to chromosome 17 came from genetic linkage studies testing segregation of NF1 and DNA genetic markers on various chromosomes. A DNA marker with two alleles, designated 1 and 2, is linked to NF1. The pedigree below shows segregation of NF1 (darkened symbols) and gives genotypes for the DNA marker for each family member.
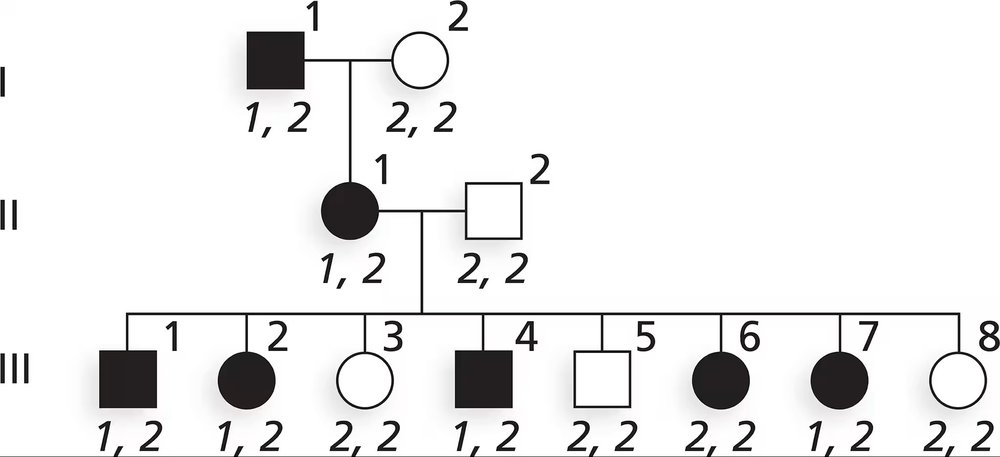
What is the estimated recombination frequency between the NF1 gene and the DNA marker?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the problem. Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant disorder linked to a DNA marker with two alleles (1 and 2). The goal is to estimate the recombination frequency between the NF1 gene and the DNA marker using the pedigree chart provided.
Step 2: Analyze the pedigree chart. Identify individuals with NF1 (darkened symbols) and their genotypes for the DNA marker. Note that the father (1,2 genotype) has NF1, while the mother (2,2 genotype) does not. The offspring's genotypes and NF1 status are also provided.
Step 3: Determine parental alleles. The father contributes either allele 1 or allele 2 to his offspring, while the mother contributes allele 2. Recombination occurs when the NF1 gene and the DNA marker are inherited separately, breaking the linkage.
Step 4: Count recombinants and non-recombinants. Compare the offspring's genotypes and NF1 status to identify recombinants (NF1 inherited with allele 2) and non-recombinants (NF1 inherited with allele 1). Count the number of each type.
Step 5: Calculate recombination frequency. Use the formula: recombination frequency = (number of recombinants / total offspring) × 100%. This provides the percentage of recombination events between the NF1 gene and the DNA marker.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to a pattern where only one copy of a mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in offspring. In the case of Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1), this means that an individual with the NF1 gene mutation has a 50% chance of passing it on to each child, regardless of the child's sex. This pattern is crucial for understanding the pedigree analysis and the inheritance of NF1.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Recombination Frequency
Recombination frequency is a measure of the likelihood that two genes will be separated during meiosis due to crossing over. It is calculated as the number of recombinant offspring divided by the total number of offspring. In genetic linkage studies, a lower recombination frequency indicates that two genes are closely linked on the same chromosome, which is essential for estimating the distance between the NF1 gene and the DNA marker in the provided pedigree.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Recombination after Single Strand Breaks
Genetic Linkage Studies
Genetic linkage studies investigate the co-segregation of genes and genetic markers within families to determine their relative positions on chromosomes. By analyzing the inheritance patterns of traits and associated markers, researchers can identify linked genes, such as the NF1 gene on chromosome 17. These studies are fundamental for mapping genetic disorders and understanding their inheritance patterns, as seen in the analysis of NF1.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square and Linkage
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Based on our discussion of the potential inaccuracy of mapping (see Figure 5.12), would you revise your answer to Problem 22? If so, how?
544
views


