Which principle is NOT used to construct a phylogenetic tree?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
22. Evolutionary Genetics
Phylogenetic Trees
Problem D.4
Textbook Question
Discuss how both gains and losses of regulatory elements may lead to human-specific traits.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by defining regulatory elements in genetics: these are DNA sequences such as enhancers, silencers, promoters, and insulators that control the expression of genes without altering the protein-coding sequence itself.
Explain that gains of regulatory elements refer to the acquisition of new regulatory sequences or the modification of existing ones, which can lead to novel patterns of gene expression unique to humans, potentially contributing to human-specific traits.
Discuss how losses of regulatory elements involve the deletion or inactivation of certain regulatory sequences, which can reduce or eliminate gene expression in specific contexts, also resulting in traits that distinguish humans from other species.
Illustrate with examples how changes in regulatory elements can affect developmental pathways, brain function, or other physiological processes, emphasizing that these changes can be subtle but have significant phenotypic effects.
Conclude by highlighting that both gains and losses of regulatory elements contribute to evolutionary divergence by altering gene expression patterns, thereby shaping human-specific traits without changing the underlying protein-coding genes.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Regulatory Elements in Genetics
Regulatory elements are DNA sequences such as enhancers, silencers, and promoters that control gene expression levels. They do not code for proteins but influence when, where, and how much a gene is expressed, playing a crucial role in development and phenotype.
Recommended video:
Guided course
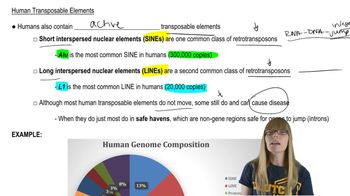
Human Transposable Elements
Gene Expression and Phenotypic Variation
Changes in gene expression, driven by regulatory elements, can lead to differences in traits without altering the underlying protein-coding genes. Variations in expression patterns contribute to phenotypic diversity, including species-specific characteristics.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Penetrance and Expressivity
Evolutionary Impact of Gains and Losses of Regulatory Elements
Gains (e.g., new enhancers) or losses (e.g., deletion of silencers) of regulatory elements can modify gene expression patterns, leading to novel traits or loss of ancestral traits. Such changes are key mechanisms in human evolution, contributing to traits unique to our species.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Transposable Elements
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
437
views
4
rank


