Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Mutations: Aneuploidy
Problem 8d
Textbook Question
If the haploid number for a plant species is 4, how many chromosomes are found in a member of the species that has one of the following characteristics? Explain your reasoning in each case.
Trisomy
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of haploid number: The haploid number (n) represents the number of chromosomes in a single set of a species' genome. For this plant species, the haploid number is given as 4, meaning n = 4.
Determine the diploid number: In diploid organisms, the total number of chromosomes is twice the haploid number. Therefore, the diploid number (2n) for this species is 2 × 4 = 8 chromosomes.
Understand trisomy: Trisomy refers to the presence of an extra chromosome in addition to the normal diploid set. This means that instead of having two copies of a particular chromosome, the organism has three copies of that chromosome.
Calculate the total number of chromosomes in a trisomic individual: Since the diploid number is 8, adding one extra chromosome for trisomy results in 8 + 1 = 9 chromosomes.
Explain the reasoning: The extra chromosome in trisomy arises due to nondisjunction during meiosis, where chromosomes fail to separate properly. This leads to an individual having one additional chromosome beyond the normal diploid set.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Haploid and Diploid Numbers
The haploid number (n) refers to the number of chromosomes in a gamete, which is half the total number of chromosomes in a diploid organism. In this case, if the haploid number for the plant species is 4, the diploid number (2n) would be 8, representing the total chromosomes in somatic cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diploid Genetics
Trisomy
Trisomy is a genetic condition where an individual has three copies of a particular chromosome instead of the usual two. This results in a total of one extra chromosome, leading to a total chromosome count of 2n + 1. For the plant species in question, this would mean having 9 chromosomes (8 diploid + 1 extra).
Recommended video:
Guided course
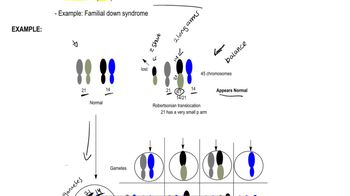
Robertsonian Translocations
Chromosome Number Calculation
To determine the chromosome number in a specific genetic condition, one must understand how to calculate the total based on the haploid and diploid numbers. For a plant with a haploid number of 4, the diploid number is 8, and in the case of trisomy, the total chromosome count becomes 9, which is essential for understanding genetic variations in this species.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Calculating Heritability
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
What evidence suggests that Down syndrome is more often the result of nondisjunction during oogenesis rather than during spermatogenesis?
811
views


