Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Down Syndrome and Its Genetic Basis
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused primarily by trisomy of chromosome 21, leading to intellectual disability and characteristic physical features. Understanding its genetic basis involves recognizing that an extra copy of chromosome 21 disrupts normal development, which is why prenatal screening and karyotyping are used to detect this condition.
Recommended video:
Down Syndrome Critical Region (DSCR)
The Down Syndrome Critical Region (DSCR) is a specific segment on chromosome 21 believed to contain genes responsible for many of the features of Down syndrome. Identifying this region helps researchers focus on key genes whose overexpression contributes to the syndrome’s phenotype, aiding in understanding and potential therapies.
Recommended video:
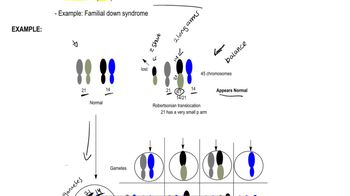
Robertsonian Translocations
Maternal Serum Screening and Karyotype Analysis
Maternal serum screening measures specific proteins and hormones in a pregnant woman's blood to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome. Karyotype analysis involves examining fetal chromosomes directly to confirm the presence of trisomy 21, providing a definitive diagnosis.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: