Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cis-regulatory Elements
Cis-regulatory elements are DNA sequences located near a gene that regulate its transcription by serving as binding sites for transcription factors. These include promoters, operators, and enhancers, which control gene expression by facilitating or blocking RNA polymerase access. Understanding these elements is essential to compare how the lac operon and GAL system control gene activity.
Recommended video:
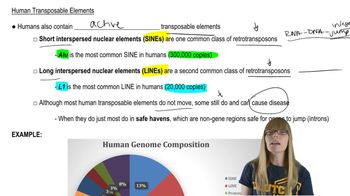
Human Transposable Elements
Lac Operon Cis-regulatory Elements
The lac operon contains key cis-regulatory elements such as the promoter, operator, and CAP binding site. The operator binds the lac repressor to inhibit transcription in the absence of lactose, while the CAP site binds an activator protein to enhance transcription when glucose is low. These elements enable tight control of lactose metabolism genes in E. coli.
Recommended video:
GAL System Cis-regulatory Elements
The GAL gene system in yeast uses upstream activating sequences (UAS) as cis-regulatory elements, which bind activator proteins like Gal4 to promote transcription. Unlike the lac operon, the GAL system relies heavily on activators and chromatin remodeling, with less emphasis on repressor binding sites, reflecting a different regulatory strategy for adapting to galactose.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: