Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromatids
Chromatids are the two identical halves of a replicated chromosome, which are joined together at a region called the centromere. During cell division, specifically in mitosis and meiosis, chromatids play a crucial role in ensuring that genetic material is accurately distributed to daughter cells. In the context of the question, the cigar-shaped structures represent chromatids that will be manipulated to model chromosome behavior during cell division.
Recommended video:
Homologous Chromosomes
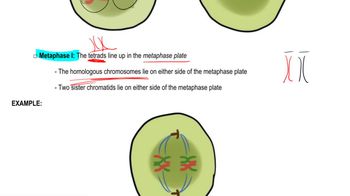
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have the same structure and carry genes for the same traits, but may have different alleles. Each pair consists of one chromosome inherited from each parent. In the exercise described, the sets of chromatids labeled 'A', 'a', 'B', 'b', 'D', and 'd' represent homologous chromosomes, which are essential for understanding genetic variation and inheritance during meiosis.
Recommended video:
Anaphase II and Telophase II
Anaphase II and Telophase II are stages of meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes. During Anaphase II, sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell, while in Telophase II, the separated chromatids reach the poles, and the cell begins to divide. Understanding these stages is crucial for visualizing how genetic material is segregated and how gametes are formed, which is the focus of the exercise in the question.
Recommended video: