If two chromosomes of a species are the same length and have similar centromere placements and yet are not homologous, what is different about them?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis
Problem 9
Textbook Question
Describe the phases of the cell cycle and the events that characterize each phase.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
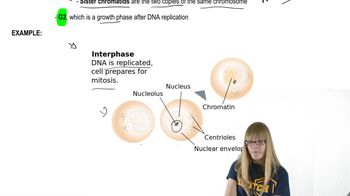
Begin by identifying the main phases of the cell cycle: Interphase (which includes G1, S, and G2 phases) and the Mitotic (M) phase.
Describe the G1 phase (Gap 1) as the period of cell growth where the cell increases in size and synthesizes proteins necessary for DNA replication.
Explain the S phase (Synthesis) as the phase where DNA replication occurs, resulting in the duplication of chromosomes to prepare for cell division.
Outline the G2 phase (Gap 2) as the final preparation phase where the cell continues to grow and produces proteins required for mitosis, while also checking for DNA replication errors.
Detail the M phase (Mitosis) as the phase where the cell undergoes nuclear division followed by cytokinesis, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells; include the subphases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and their key events.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phases of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle consists of distinct phases: G1 (cell growth), S (DNA synthesis), G2 (preparation for mitosis), and M (mitosis and cytokinesis). These phases ensure proper cell growth, DNA replication, and division into two daughter cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bacteriophage Life Cycle
Events in Interphase
Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases, where the cell grows, duplicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis. During S phase, DNA replication occurs, ensuring each daughter cell receives an identical genome.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Probability
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division, consisting of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, leading to equal chromosome segregation. Cytokinesis follows, dividing the cytoplasm and completing cell division.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mitosis Steps
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
822
views


