Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Homologous Chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism, one inherited from each parent. They carry the same genes at the same loci but may have different alleles. During meiosis, these chromosomes undergo pairing and recombination, which is crucial for genetic diversity. Understanding their behavior is essential for grasping how alleles segregate during gamete formation.
Recommended video:
Mendel's Law of Segregation
Mendel's Law of Segregation states that during the formation of gametes, the two alleles for a trait separate from each other so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene. This principle explains how offspring inherit one allele from each parent. The law is illustrated during meiosis when homologous chromosomes are separated, ensuring that each gamete receives only one allele from each gene pair.
Recommended video:
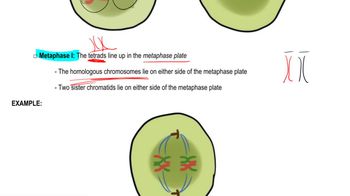
Meiosis Stages
Meiosis consists of two rounds of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II. The segregation of alleles occurs during anaphase I of meiosis I, when homologous chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. This separation ensures that each gamete receives one allele from each pair of homologous chromosomes, aligning with Mendel's law of segregation and contributing to genetic variation in offspring.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: