In this chapter, we have focused on genetic systems present in bacteria and on the viruses that use bacteria as hosts (bacteriophages). In particular, we discussed mechanisms by which bacteria and their phages undergo genetic recombination, which allows geneticists to map bacterial and bacteriophage chromosomes. In the process, we found many opportunities to consider how this information was acquired. From the explanations given in the chapter, what answers would you propose to the following questions? How do we know that in bacteriophage T4 the rII locus is subdivided into two regions, or cistrons?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteriophage Genetics
Problem 8
Textbook Question
What is a prophage, and how is a prophage formed?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
A prophage is a form of a bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria) where the viral DNA is integrated into the bacterial host's genome. It remains dormant and does not cause immediate lysis of the host cell.
The formation of a prophage begins when a bacteriophage infects a bacterial cell and injects its DNA into the host.
Once inside the bacterial cell, the viral DNA can either enter the lytic cycle (leading to the destruction of the host cell) or the lysogenic cycle, where it integrates into the bacterial genome.
During the lysogenic cycle, the viral DNA integrates into the bacterial chromosome through a process called site-specific recombination. This integration is facilitated by enzymes encoded by the bacteriophage, such as integrase.
After integration, the viral DNA becomes a prophage and is replicated along with the bacterial genome during cell division. It remains dormant until certain conditions trigger its reactivation, leading to the lytic cycle.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Prophage Definition
A prophage is a form of a bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria) that has integrated its genetic material into the host bacterium's chromosome. This integration allows the viral DNA to be replicated along with the host's DNA during cell division, remaining dormant until certain conditions trigger its activation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Plaques and Experiments
Lysogenic Cycle
The lysogenic cycle is one of the two main life cycles of bacteriophages, where the virus integrates its DNA into the host genome, forming a prophage. During this cycle, the prophage can remain inactive for long periods, allowing the host bacterium to reproduce normally while carrying the viral genetic material.
Recommended video:
Guided course
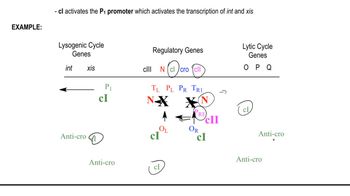
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Induction of Prophage
Induction is the process by which a prophage is activated to enter the lytic cycle, leading to the production of new viral particles. This can occur due to various environmental factors, such as stress or damage to the host cell, which trigger the prophage to excise itself from the host genome and begin replicating.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Plaques and Experiments

 3:44m
3:44mWatch next
Master Plaques and Experiments with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
407
views
