What is a prophage, and how is a prophage formed?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteriophage Genetics
Problem 14
Textbook Question
Seven deletion mutations (1 to 7 in the table below) are tested for their ability to form wild-type recombinants with five point mutations (a to e). The symbol "+" indicates that wild-type recombination occurs, and "-" indicates that wild types are not formed. Use the data to construct a genetic map of the order of point mutations, and indicate the segment deleted by each deletion mutation.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Analyze the table to determine the relationship between deletion mutations (1 to 7) and point mutations (a to e). The '+' indicates that recombination restores the wild-type phenotype, while '-' indicates no recombination occurs.
Step 2: Identify the regions deleted by each deletion mutation. For example, if a deletion mutation fails to recombine with a point mutation (indicated by '-'), it suggests that the point mutation lies within the deleted region.
Step 3: Use the patterns of '+' and '-' to infer the order of point mutations. For instance, if deletion mutation 1 fails to recombine with 'a' but recombines with 'b', 'c', 'd', and 'e', then 'a' is likely within the region deleted by mutation 1.
Step 4: Compare the deletion mutations to determine overlapping and non-overlapping regions. For example, deletion mutation 2 recombines with 'a' and 'd' but fails with 'b', 'c', and 'e', suggesting a different deleted segment compared to mutation 1.
Step 5: Construct a genetic map by arranging the point mutations (a to e) in order based on their recombination patterns with the deletion mutations. Indicate the segments deleted by each mutation on the map, ensuring consistency with the data provided in the table.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
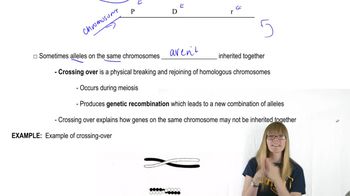
Genetic Mapping
Genetic mapping is the process of determining the relative positions of genes on a chromosome. It involves analyzing recombination frequencies between mutations to infer their order and distance. In this context, the data from deletion mutations and point mutations will help construct a genetic map that illustrates how these mutations interact and their spatial arrangement.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mapping Overview
Recombination
Recombination is a genetic process where genetic material is exchanged between different chromosomes or within the same chromosome, leading to new allele combinations. In the provided data, the presence of wild-type recombinants (indicated by '+') suggests successful recombination between deletion mutations and point mutations, which is crucial for understanding gene interactions and mapping.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Recombination after Single Strand Breaks
Deletion Mutations
Deletion mutations involve the loss of a segment of DNA, which can affect gene function and expression. In the context of the question, the seven deletion mutations are tested to see how they influence the formation of wild-type recombinants with point mutations. Understanding which segments are deleted helps in determining the functional relationships between the genes involved.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Deletions

 3:44m
3:44mWatch next
Master Plaques and Experiments with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1233
views
