Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
X-linked Inheritance
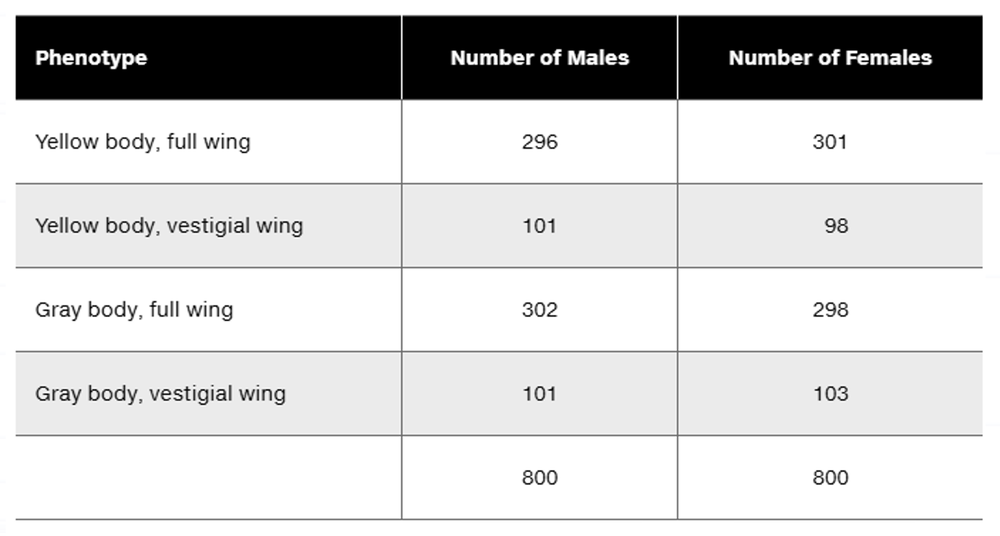
X-linked inheritance refers to genes located on the X chromosome, which affects males and females differently due to their sex chromosome composition (XY in males, XX in females). In this case, the yellow body trait is X-linked recessive, meaning males express the trait if they inherit the recessive allele, while females require two copies. Understanding this helps predict phenotypic ratios in progeny.
Recommended video:
Autosomal Inheritance
Autosomal inheritance involves genes located on non-sex chromosomes, inherited equally by males and females. The vestigial wing trait is autosomal recessive, so individuals must inherit two recessive alleles to express the trait. This concept is crucial for analyzing the segregation of wing phenotypes independent of sex.
Recommended video:
Dihybrid Cross and Phenotypic Ratios
A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of two traits simultaneously, predicting offspring phenotypes based on parental genotypes. The table shows four phenotypic classes with roughly equal numbers, indicating independent assortment of the X-linked and autosomal traits. Understanding how to interpret these ratios is key to deducing parental and progeny genotypes.
Recommended video: