Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
11. Translation
The Genetic Code
Problem 1d
Textbook Question
How were the experimentally derived triplet codon assignments verified in studies using bacteriophage MS2?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of triplet codon assignments: The genetic code is composed of nucleotide triplets (codons) that correspond to specific amino acids. These assignments were experimentally derived using techniques such as in vitro translation systems and synthetic RNA templates.
Learn about bacteriophage MS2: MS2 is an RNA virus that infects bacteria. Its genome is composed of single-stranded RNA, which can be directly translated into proteins. This makes it an excellent model for studying the genetic code and verifying codon assignments.
Explore the experimental approach: Researchers used the MS2 RNA genome to study codon assignments. By analyzing the sequence of the MS2 RNA and the corresponding amino acid sequence of its proteins, they could verify which codons corresponded to specific amino acids.
Understand the role of mutational analysis: Mutations were introduced into the MS2 RNA genome, and the resulting changes in the protein sequence were observed. This helped confirm the relationship between specific codons and their corresponding amino acids.
Consider the use of sequencing and comparison: The nucleotide sequence of MS2 RNA was compared to the amino acid sequence of its proteins. This direct correlation provided strong evidence for the experimentally derived triplet codon assignments.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Triplet Codon Assignments
Triplet codon assignments refer to the genetic code's specification of how sequences of three nucleotides (codons) correspond to specific amino acids during protein synthesis. Each codon is a unique combination of the four nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil in RNA), and understanding these assignments is crucial for deciphering how genetic information translates into functional proteins.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Genetic Code
Bacteriophage MS2
Bacteriophage MS2 is a type of virus that infects bacteria, specifically Escherichia coli. It was one of the first organisms used to study the genetic code due to its relatively simple RNA genome, which allowed researchers to manipulate and analyze its genetic material. Studies involving MS2 provided key insights into how codons are read and translated into proteins.
Recommended video:
Guided course
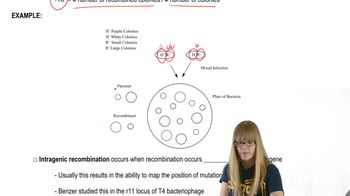
Mapping Bacteriophages
Experimental Verification Methods
Experimental verification methods in genetics involve techniques used to confirm hypotheses about genetic code and its translation. In the context of MS2, researchers employed methods such as mutagenesis and subsequent analysis of the resulting phenotypes to demonstrate how specific codons correspond to particular amino acids, thereby validating the triplet codon assignments through empirical evidence.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Methods for Analyzing DNA and RNA
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
The nucleic acid sequence in mRNA is determined by which of the following?
3
views


