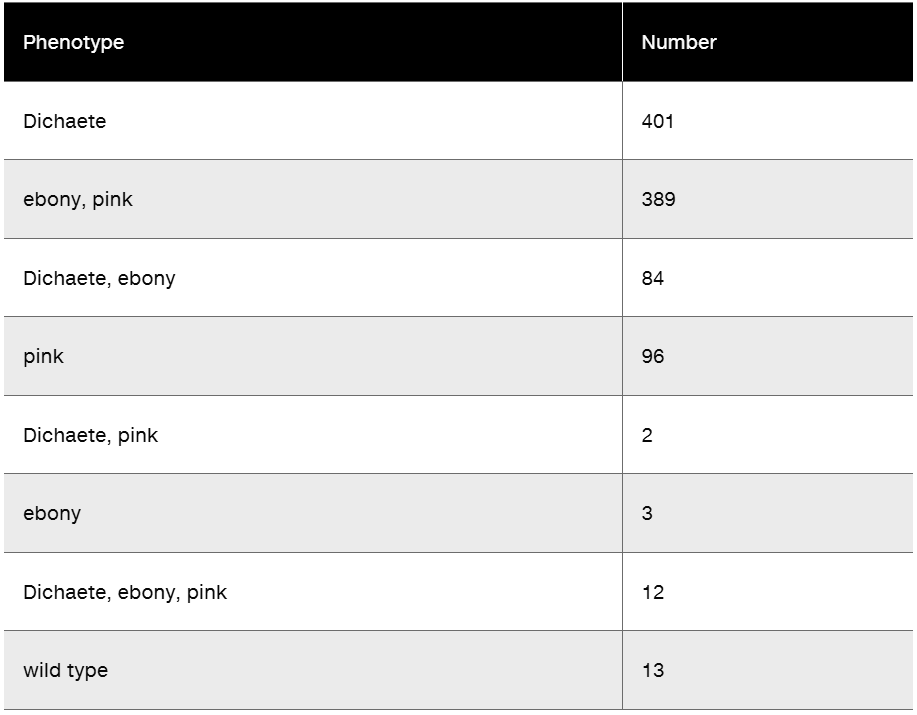
Researchers cross a corn plant that is pure-breeding for the dominant traits colored aleurone (C1), full kernel (Sh), and waxy endosperm (Wx) to a pure-breeding plant with the recessive traits colorless aleurone (c1), shrunken kernel (sh), and starchy (wx). The resulting F₁ plants were crossed to pure-breeding colorless, shrunken, starchy plants. Counting the kernels from about 30 ears of corn yields the following data.
Calculate the recombination frequencies between the gene pairs.