Three gene pairs located on separate autosomes determine flower color and shape as well as plant height. The first pair exhibits incomplete dominance, where the color can be red, pink (the heterozygote), or white. The second pair leads to personate (dominant) or peloric (recessive) flower shape, while the third gene pair produces either the dominant tall trait or the recessive dwarf trait. Homozygous plants that are red, personate, and tall are crossed to those that are white, peloric, and dwarf. Determine the F₁ genotype(s) and phenotype(s). If the F₁ plants are interbred, what proportion of the offspring will exhibit the same phenotype as the F₁ plants?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Trihybrid Cross
Problem 16b
Textbook Question
In a diploid plant species, an F₁ with the genotype Gg Ll Tt is test-crossed to a pure-breeding recessive plant with the genotype gg ll tt. The offspring genotypes are as follows:
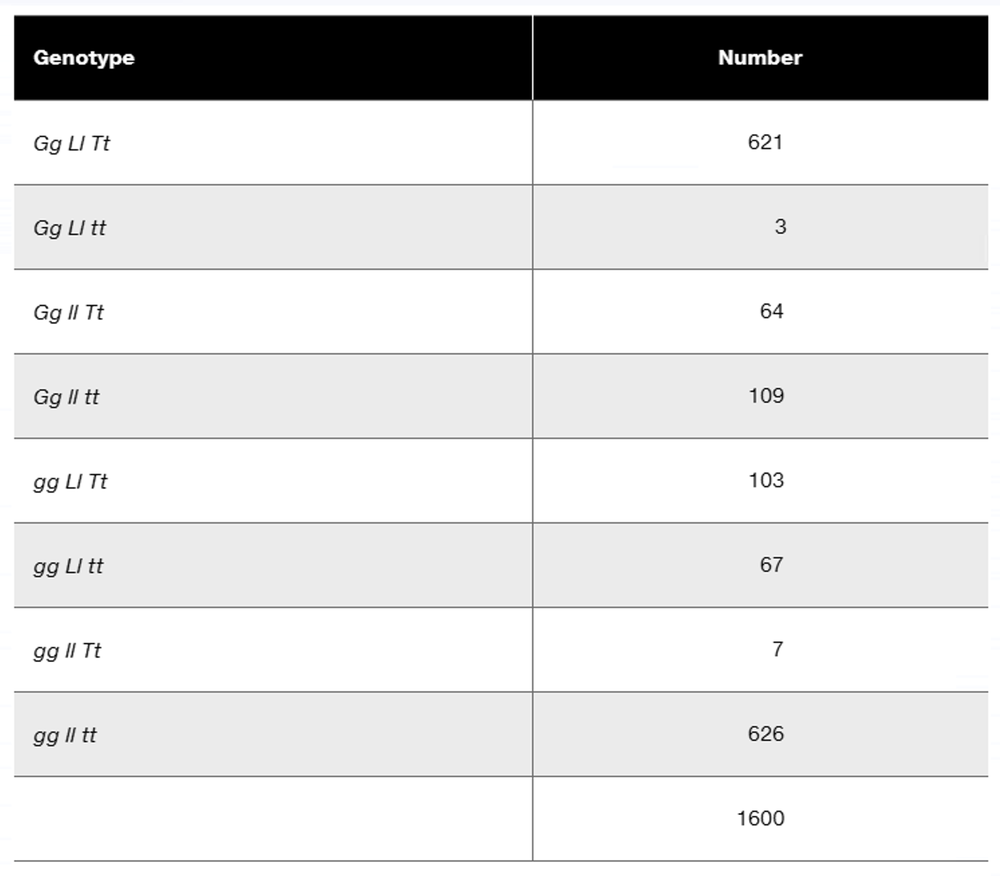
Calculate the recombination frequency between each pair of genes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the parental genotypes and offspring genotypes. The parental genotypes are Gg Ll Tt (heterozygous for all three genes) and gg ll tt (homozygous recessive for all three genes). The offspring genotypes and their counts are provided in the table.
Step 2: Determine which offspring genotypes represent parental types and which represent recombinant types. Parental types will have the same combinations of alleles as the parents (Gg Ll Tt and gg ll tt), while recombinant types will have new combinations of alleles due to crossing over.
Step 3: Calculate the total number of recombinant offspring for each pair of genes. For example, to calculate recombination frequency between G and L, sum the counts of offspring with recombinant genotypes for these two genes.
Step 4: Use the formula for recombination frequency: \( \text{Recombination Frequency} = \frac{\text{Number of Recombinant Offspring}}{\text{Total Number of Offspring}} \times 100 \). Apply this formula to each pair of genes (G and L, L and T, G and T).
Step 5: Interpret the recombination frequencies. Frequencies below 50% indicate linkage between the genes, while frequencies close to 50% suggest independent assortment. This helps determine the genetic distance between the genes.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Test Cross
A test cross is a genetic cross between an individual with an unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual. This method helps determine the genotype of the unknown parent by analyzing the phenotypes of the offspring. In the context of the question, the F₁ plant (Gg Ll Tt) is crossed with a pure-breeding recessive plant (gg ll tt) to reveal the genetic contributions of the dominant alleles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trihybrid Cross
Recombination Frequency
Recombination frequency is a measure of the likelihood that two genes will be separated during meiosis due to crossing over. It is calculated by dividing the number of recombinant offspring by the total number of offspring and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. This frequency provides insights into the genetic linkage between genes, with lower frequencies indicating closer linkage.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Recombination after Single Strand Breaks
Linkage and Genetic Mapping
Linkage refers to the tendency of genes located close to each other on a chromosome to be inherited together. Genetic mapping uses recombination frequencies to determine the relative positions of genes on a chromosome. By analyzing the offspring genotypes from the test cross, one can infer the distances between genes G, L, and T, which aids in constructing a genetic map.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square and Linkage
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
788
views


