Which of the following gametes cannot be formed from the genotype HhJjKK?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Understanding Independent Assortment
Problem 5a
Textbook Question
In tomato plants, purple leaf color is controlled by a dominant allele A, and green leaf by a recessive allele a. At another locus, hairy leaf H is dominant to hairless leaf h. The genes for leaf color and leaf texture are separated by 16 m.u. on chromosome 5. On chromosome 4, a gene controlling leaf shape has two alleles: a dominant allele C that produces cut-leaf shape and a recessive allele c that produces potato-shaped leaves.
The cross of a purple, hairy, cut plant heterozygous at each gene to a green, hairless potato plant produces the following progeny:
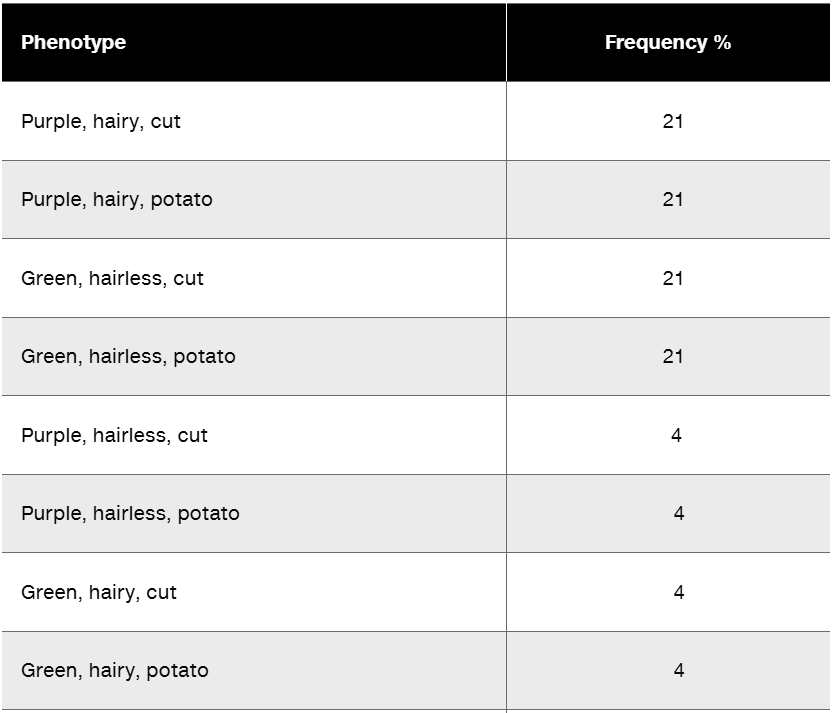
Give the genotypes of parental and progeny plants in this experiment.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the parental genotypes. The problem states that the purple, hairy, cut plant is heterozygous at each gene, so its genotype is AaHhCc. The green, hairless, potato plant is homozygous recessive for all traits, so its genotype is aahhcc.
Step 2: Determine the possible gametes for each parent. The heterozygous parent (AaHhCc) can produce 8 types of gametes (AHC, AHc, AhC, Ahc, aHC, aHc, ahC, ahc) due to independent assortment. The homozygous recessive parent (aahhcc) can only produce one type of gamete (ahc).
Step 3: Analyze the progeny phenotypes and frequencies. The progeny phenotypes and their frequencies suggest that the genes A and H are linked, as the parental phenotypes (purple, hairy, cut and green, hairless, potato) are more frequent (21% each) than the recombinant phenotypes (e.g., purple, hairless, cut at 4%).
Step 4: Use the recombination frequency to confirm linkage. The recombination frequency between A and H is given as 16 m.u. (map units), which corresponds to 16% recombination. This matches the sum of the recombinant phenotypes (4% + 4% + 4% + 4% = 16%).
Step 5: Assign genotypes to the progeny. For each phenotype, deduce the genotype based on the traits: (1) Purple, hairy, cut = AaHhCc, (2) Purple, hairy, potato = AaHhcc, (3) Green, hairless, cut = aahhCc, (4) Green, hairless, potato = aahhcc, (5) Purple, hairless, cut = AaHhCc (recombinant), (6) Purple, hairless, potato = AaHhcc (recombinant), (7) Green, hairy, cut = aahhCc (recombinant), (8) Green, hairy, potato = aahhcc (recombinant).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
In genetics, alleles are different forms of a gene that can exist at a specific locus on a chromosome. Dominant alleles, represented by uppercase letters (e.g., A, H, C), mask the expression of recessive alleles, represented by lowercase letters (e.g., a, h, c). In this question, the purple leaf color (A) is dominant over green (a), and hairy leaves (H) are dominant over hairless (h). Understanding this concept is crucial for predicting phenotypic ratios in offspring.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Genotype and Phenotype
The genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, specifically the alleles present at a given locus, while the phenotype is the observable physical or biochemical characteristics resulting from the genotype. For example, a plant with the genotype AaHhCc can exhibit a purple, hairy, cut phenotype. Analyzing the genotypes of the parental plants and their progeny helps in understanding inheritance patterns and predicting the traits of future generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gamete Genotypes
Linkage and Recombination
Linkage refers to the tendency of genes located close to each other on the same chromosome to be inherited together, while recombination is the process that can separate linked genes during meiosis. In this scenario, the genes for leaf color and texture are separated by 16 map units (m.u.), indicating a degree of linkage. Understanding the effects of linkage and recombination is essential for predicting the expected ratios of phenotypes in the progeny from the cross described.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square and Linkage

 4:58m
4:58mWatch next
Master Gamete Genetics and Independent Assortment with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
646
views
5
rank
