What two essential criteria must be met in order to execute a successful mapping cross?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Crossing Over and Recombinants
Problem 18
Textbook Question
In Drosophila, two mutations, Stubble (Sb) and curled (cu), are linked on chromosome III. Stubble is a dominant gene that is lethal in a homozygous state, and curled is a recessive gene. If a female of the genotype
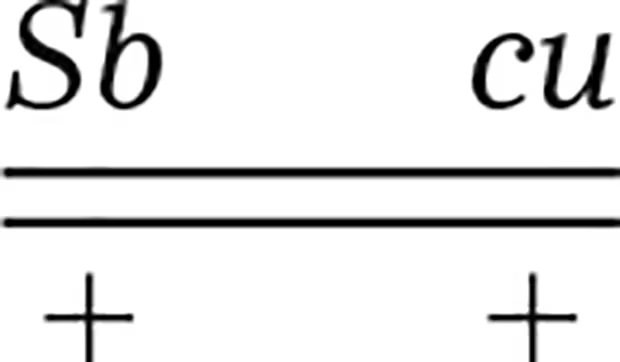
is to be mated to detect recombinants among her offspring, what male genotype would you choose as a mate?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the female genotype given: she is heterozygous for the linked genes Stubble (Sb) and curled (cu), with the genotype \( \frac{Sb\;cu}{+\;+} \). This means one chromosome carries both mutant alleles (Sb and cu), and the homologous chromosome carries the wild-type alleles (+ and +).
Recall that Stubble (Sb) is dominant and lethal in homozygous form, while curled (cu) is recessive. This affects which offspring survive and how phenotypes appear.
To detect recombinants among offspring, you need to mate the female with a male whose genotype allows clear identification of recombinant phenotypes. The male should be homozygous recessive for both genes, i.e., \( \frac{+\;+}{+\;+} \) but carrying recessive alleles for both traits, so that any recombinant gametes from the female can be distinguished in the progeny.
In Drosophila genetics, the standard practice is to use a male that is homozygous recessive for both genes (\( sb\;cu \)) so that all offspring phenotypes directly reflect the female's gametes, allowing detection of parental and recombinant types.
Therefore, the male genotype to choose is \( \frac{sb\;cu}{sb\;cu} \), which is homozygous recessive for both Stubble and curled, enabling clear scoring of recombinant offspring.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Linked Genes and Recombination
Linked genes are located close together on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together. Recombination occurs during meiosis when crossing over between homologous chromosomes can separate linked genes, producing new allele combinations. Detecting recombinants helps map gene distances and understand linkage.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sex-Linked Genes
Dominant Lethal Alleles
A dominant lethal allele causes death when present in a homozygous state, preventing individuals with two copies from surviving. In heterozygotes, the dominant trait is expressed without lethality. This affects genotype frequencies and must be considered when predicting offspring genotypes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Test Cross and Choice of Mate Genotype
A test cross involves mating an individual with a known genotype to a homozygous recessive individual to reveal the genotype of the first parent through offspring phenotypes. Choosing a male homozygous recessive for both genes allows detection of recombinant offspring by their phenotypes, clarifying linkage and recombination.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Monohybrid Cross
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
616
views


