Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enhancer Sequences
Enhancer sequences are regulatory DNA elements that can significantly increase the transcription of specific genes. They function by binding transcription factors, which then interact with the transcription machinery at the promoter region, facilitating the recruitment of RNA polymerase. Enhancers can be located far from the gene they regulate and can work in a tissue-specific manner, allowing for precise control of gene expression.
Recommended video:
Transcription in Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes
In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves complex regulation, including the use of enhancers, silencers, and various transcription factors. In contrast, prokaryotic transcription occurs in the cytoplasm and is generally simpler, with RNA polymerase directly binding to the promoter without the need for additional regulatory elements like enhancers. This fundamental difference reflects the complexity of eukaryotic gene regulation.
Recommended video:
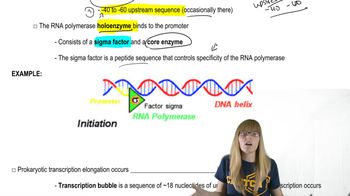
Prokaryotic Transcription
Gene Regulation
Gene regulation refers to the mechanisms that control the expression of genes, determining when and how much of a gene product is made. In eukaryotes, this involves a variety of elements, including enhancers, silencers, and transcription factors, which work together to fine-tune gene expression in response to developmental cues and environmental signals. Effective gene regulation is crucial for cellular function and organismal development.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 9:16m
9:16m