Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Prototrophy and Auxotrophy
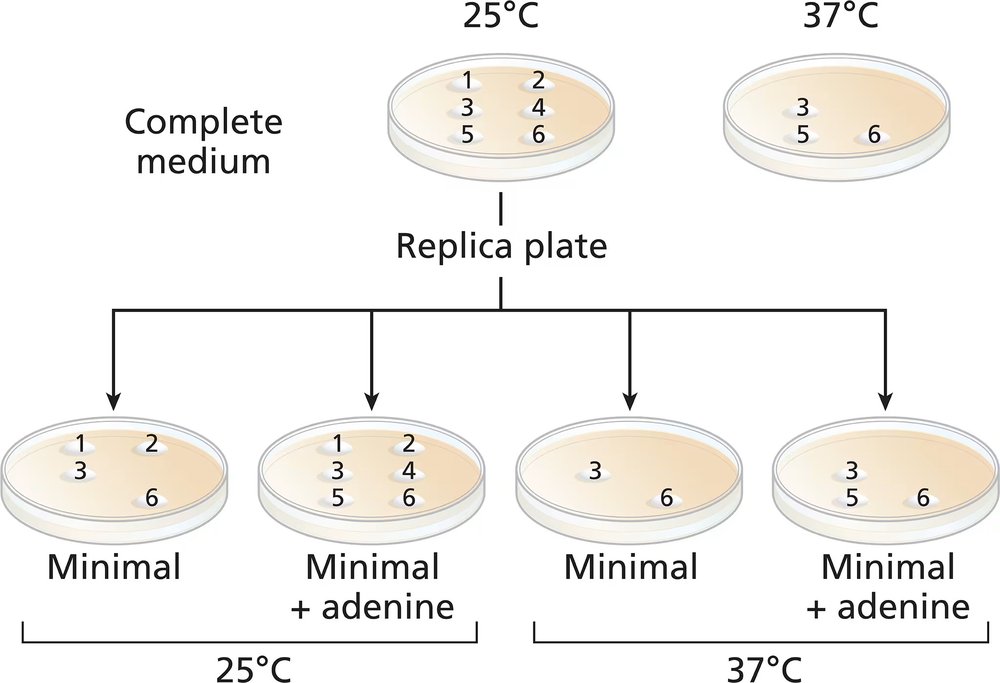
Prototrophy refers to the ability of an organism to synthesize all essential compounds needed for growth from basic nutrients, while auxotrophy indicates a mutation that prevents the organism from synthesizing a specific compound, requiring it to be supplied in the growth medium. In yeast, prototrophic strains can grow on minimal media, whereas auxotrophic strains need additional nutrients, such as adenine, to thrive.
Recommended video:
Bacteria in the Laboratory
Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis is the process of inducing mutations in an organism's DNA, often using chemical agents like ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS). This technique is commonly used in genetics to create variations in traits, allowing researchers to study gene function and identify mutations that affect growth and metabolism, such as those leading to prototrophy or auxotrophy.
Recommended video:
Temperature Effects on Yeast Growth
Temperature significantly influences yeast growth and metabolic activity. Saccharomyces cerevisiae typically grows well at 37°C but can also grow at lower temperatures, such as 25°C. Understanding how temperature affects growth is crucial for interpreting experimental results, as it can impact the expression of mutations and the overall viability of yeast colonies on different media.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

