The table given here lists the arrangement of alleles of linked genes in dihybrid organisms, the recombination frequency between the genes, and specific gamete genotypes. Using the information provided, determine the expected frequency of the listed gametes. Assume one map unit equals 1% recombination and, when three genes are involved, interference is zero.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 18a
Textbook Question
The Rh blood group in humans is determined by a gene on chromosome 1. A dominant allele produces Rh+ blood type, and a recessive allele generates Rh-. Elliptocytosis is an autosomal dominant disorder that produces abnormally shaped red blood cells that have a short life span resulting in hereditary anemia. A large family with elliptocytosis is tested for genetic linkage of Rh blood group and the disease. The lod score data below are obtained for the family.
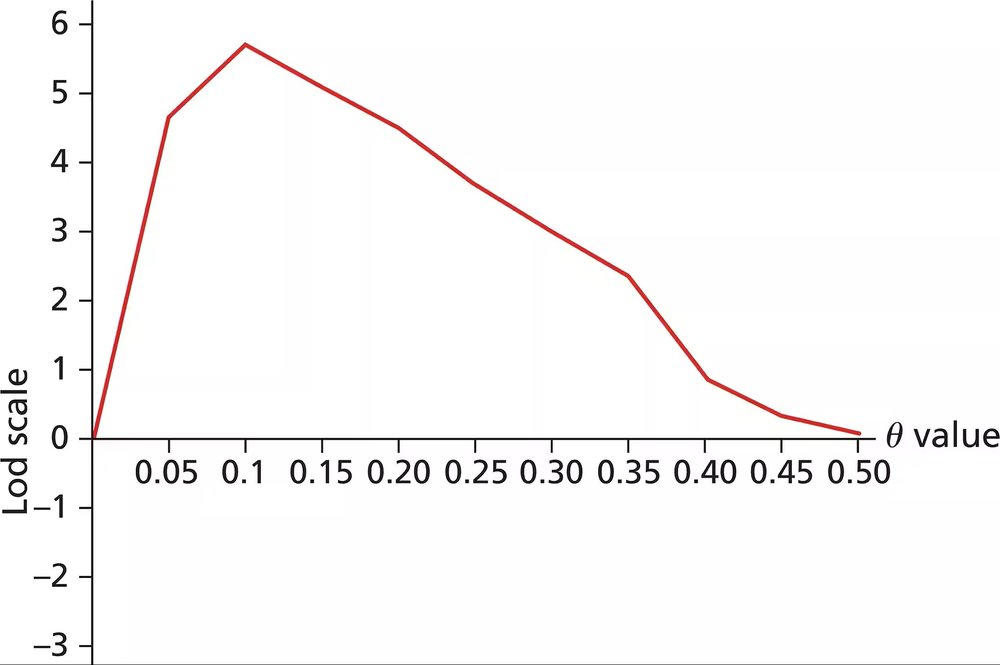
From these data, can you conclude that Rh and elliptocytosis loci are genetically linked in this family? Why or why not?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the graph provided, which shows the lod score plotted against recombination fraction (θ). The lod score is a statistical measure used to determine the likelihood of genetic linkage between two loci.
Identify the peak lod score on the graph. In this case, the peak lod score is approximately 6, which occurs at a recombination fraction (θ) of around 0.1.
Recall the threshold for genetic linkage: a lod score greater than 3 is considered strong evidence for linkage. Since the peak lod score is 6, this strongly suggests that the Rh blood group and elliptocytosis loci are genetically linked.
Interpret the recombination fraction (θ) value at the peak lod score. A θ value of 0.1 indicates that the loci are relatively close on the chromosome, with a 10% chance of recombination occurring between them during meiosis.
Conclude that the data supports genetic linkage between the Rh blood group and elliptocytosis loci in this family, based on the high lod score and low recombination fraction observed in the graph.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Genetic Linkage
Genetic linkage refers to the tendency of genes located close to each other on a chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis. This occurs because the physical proximity of genes reduces the likelihood of recombination between them. The strength of linkage can be assessed using lod scores, which compare the likelihood of observing the data under the hypothesis of linkage versus no linkage.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square and Linkage
Lod Score
A lod score (logarithm of the odds) is a statistical measure used to evaluate the likelihood of genetic linkage between two loci. A lod score greater than 3 suggests significant evidence for linkage, while a score less than -2 indicates evidence against linkage. The graph provided likely shows lod scores across different recombination fractions, helping to determine the relationship between the Rh blood group and elliptocytosis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Formation of Plant Gametes
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Autosomal dominant inheritance is a pattern where only one copy of a dominant allele is needed for the trait or disorder to manifest. In the case of elliptocytosis, the presence of a single mutated allele leads to the abnormal red blood cell shape. Understanding this inheritance pattern is crucial for interpreting the genetic data and assessing the likelihood of the disorder being linked to the Rh blood group.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
519
views


