The National Institutes of Health created the Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) to increase transparency by publicly sharing information about the utility of their tests, research for the general public, patients, health-care workers, genetic counselors, insurance companies, and others. The Registry is intended to provide better information to patients, but companies involved in genetic testing are not required to participate. Should company participation be mandatory? Why or why not? Explain your answers.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
18. Molecular Genetic Tools
Methods for Analyzing DNA
Problem 21c
Textbook Question
You have isolated another cDNA clone of the CRABS CLAW gene from a cDNA library.. The cDNA was directionally cloned using the EcoRI and XhoI sites. You sequence the recombinant plasmid using primers complementary to the T7 and T3 promoter sites flanking the MCS. The first 30 to 60 bases of sequence are usually discarded since they tend to contain errors.
Can you identify which sequence portions are derived from the vector (specifically the MCS) and which are derived from the cDNA clone?
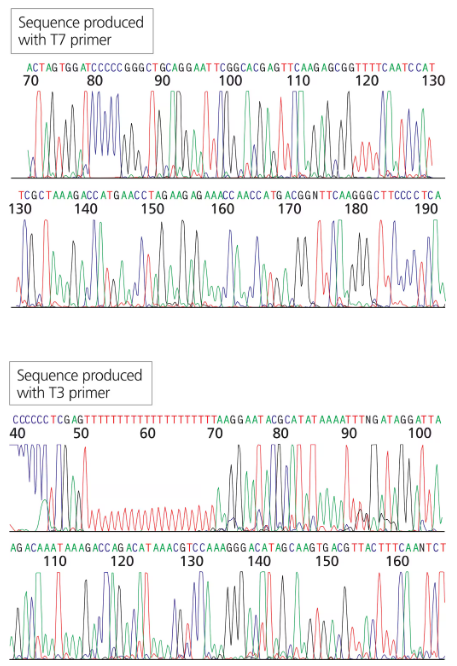
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of directional cloning. Directional cloning ensures that the cDNA is inserted into the vector in a specific orientation using restriction enzyme sites, in this case, EcoRI and XhoI. This allows the cDNA to be flanked by known sequences in the vector, such as the T7 and T3 promoter sites.
Step 2: Review the structure of the vector and the multiple cloning site (MCS). The MCS contains several restriction enzyme recognition sites, including EcoRI and XhoI, which are used for inserting the cDNA. The sequence of the MCS is known and can be compared to the sequence obtained from the recombinant plasmid.
Step 3: Analyze the sequencing data obtained using primers complementary to the T7 and T3 promoter sites. The sequencing will start from these promoter sites and proceed into the MCS and the inserted cDNA. Discard the first 30 to 60 bases of sequence due to potential errors, as mentioned in the problem.
Step 4: Compare the sequence obtained from the recombinant plasmid to the known sequence of the vector's MCS. Identify the portions of the sequence that match the MCS, as these are derived from the vector. The remaining sequence, which does not match the MCS, is derived from the cDNA clone.
Step 5: Confirm the orientation and boundaries of the cDNA insert by checking the presence of EcoRI and XhoI sites flanking the cDNA. This ensures that the cDNA was directionally cloned and helps distinguish vector-derived sequences from cDNA-derived sequences.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
cDNA Cloning
cDNA cloning involves synthesizing complementary DNA (cDNA) from messenger RNA (mRNA) using the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This process allows researchers to create DNA copies of expressed genes, which can then be inserted into vectors for further study. Understanding cDNA cloning is essential for identifying gene sequences and analyzing gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genetic Cloning
Restriction Enzymes and MCS
Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut DNA at specific sequences, allowing for the insertion of foreign DNA into plasmids. The Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) is a region within a vector that contains several unique restriction sites, facilitating the directional cloning of DNA fragments. Recognizing the MCS is crucial for distinguishing between vector-derived and insert-derived sequences in recombinant DNA.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers
Sequencing and Error Management
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. In sequencing, the initial bases are often discarded due to potential errors introduced during amplification or sequencing. Understanding the importance of quality control in sequencing helps in accurately identifying which portions of the sequence correspond to the vector and which correspond to the cDNA insert.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sequencing Difficulties

 7:40m
7:40mWatch next
Master Methods for Analyzing DNA and RNA with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
468
views
