How is positional information provided along the anterior–posterior axis in Drosophila? What are the functions of bicoid and nanos?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
14. Genetic Control of Development
Developmental Patterning Genes
Problem 5b
Textbook Question
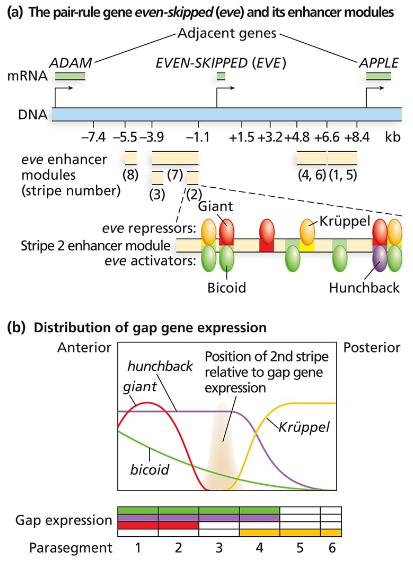
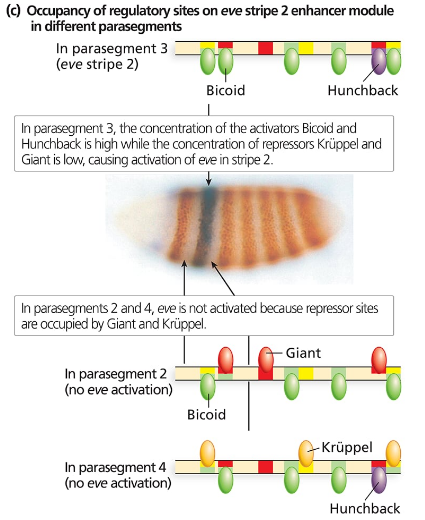
Consider the even-skipped regulatory sequences in Figure 18.9.
Consider the binding sites for gap proteins and Bicoid in the stripe 2 enhancer module. What sites are occupied in parasegments 2, 3, and 4, and how does this result in expression or no expression?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the biological context—'even-skipped' (eve) is a segmentation gene in Drosophila, and its stripe 2 enhancer module controls expression in specific parasegments by integrating inputs from gap proteins and Bicoid, which are transcription factors that bind to regulatory DNA sequences.
Step 2: Identify the binding sites for gap proteins (such as Hunchback, Kruppel, Giant) and Bicoid within the stripe 2 enhancer module, noting which proteins act as activators and which act as repressors for eve expression.
Step 3: For each parasegment (2, 3, and 4), determine the presence or absence of these proteins based on their expression gradients and domains, then infer which binding sites are occupied by activators or repressors in that parasegment.
Step 4: Analyze how the combination of occupied activator and repressor sites in each parasegment influences the transcriptional activity of the stripe 2 enhancer—activator binding promotes expression, while repressor binding inhibits it.
Step 5: Conclude for each parasegment whether eve stripe 2 is expressed or not, based on the net effect of bound proteins at the enhancer, explaining how the spatial pattern of protein binding leads to the observed stripe pattern.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Even-skipped (eve) Stripe 2 Enhancer Module
The even-skipped gene contains specific regulatory DNA sequences called enhancers that control its expression in distinct stripes during embryonic development. The stripe 2 enhancer integrates inputs from various transcription factors to activate eve expression precisely in parasegment 2. Understanding this module is key to linking protein binding patterns to spatial gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription
Gap Proteins and Bicoid as Transcriptional Regulators
Gap proteins (such as Kruppel and Giant) and Bicoid are maternal and zygotic transcription factors that bind to specific sites on enhancers. Bicoid generally acts as an activator, while gap proteins can act as activators or repressors depending on context. Their binding patterns in different parasegments determine whether the target gene is expressed or repressed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proteins
Spatial Regulation of Gene Expression in Parasegments
Parasegments are embryonic units with distinct gene expression profiles. The combination of transcription factors bound to the stripe 2 enhancer varies across parasegments 2, 3, and 4, leading to differential gene expression. This spatial regulation ensures that even-skipped is expressed only where activators dominate and repressors are absent or minimal.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Penetrance and Expressivity
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
501
views


