In Barbara McClintock's study of corn, which of the following kernel phenotypes did she find was due to transposable elements?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
16. Transposable Elements
Discovery of Transposable Elements
Problem 18
Textbook Question
How are flanking direct repeat sequences created by transposition?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of transposition: Transposition is the movement of transposable elements (TEs) within the genome. These elements can insert themselves into new locations, often creating structural changes in the DNA sequence.
Learn about flanking direct repeats: Flanking direct repeats are short, identical sequences found on both sides of a transposable element after it inserts into the genome. These repeats are not part of the transposable element itself but are created during the insertion process.
Examine the mechanism of insertion: When a transposable element inserts into a target site, the target DNA is cleaved asymmetrically, creating single-stranded overhangs. These overhangs are complementary and will later be filled in during DNA repair.
Understand the role of DNA polymerase: After the transposable element is inserted, DNA polymerase fills in the single-stranded gaps created by the asymmetric cleavage. This process duplicates the sequence at the target site, resulting in the flanking direct repeats.
Recognize the significance of flanking direct repeats: These repeats are a hallmark of transposition and can be used to identify the presence and activity of transposable elements in the genome. They also provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of transposition.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transposition
Transposition is the process by which a segment of DNA, known as a transposon or 'jumping gene', moves from one location in the genome to another. This movement can occur through a 'cut and paste' mechanism or a 'copy and paste' mechanism, leading to the insertion of the transposon at a new site. Understanding transposition is crucial for grasping how flanking direct repeat sequences are formed.
Recommended video:
Guided course
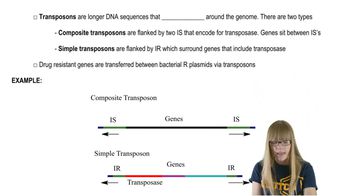
Prokaryotic Transposable Elements
Flanking Direct Repeat Sequences
Flanking direct repeat sequences are short, identical sequences of DNA that are found on either side of a transposon after it has inserted into a new location. These repeats are created during the transposition process when the transposon integrates into the target DNA, causing the host DNA to be cut and then repaired, resulting in the duplication of the adjacent sequences. This phenomenon is a hallmark of transposable elements.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sequencing Difficulties
DNA Repair Mechanisms
DNA repair mechanisms are cellular processes that correct damage to the DNA structure. When a transposon inserts itself into a new location, the host cell's repair machinery is activated to fix the breaks in the DNA. This repair often results in the duplication of the sequences adjacent to the insertion site, leading to the formation of flanking direct repeat sequences, which are essential for understanding the impact of transposition on genomic architecture.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Repair Pathways
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice


