In an assessment of learning in Drosophila, flies were trained to avoid certain olfactory cues. In one population, a mean of 8.5 trials was required. A subgroup of this parental population that was trained most quickly (mean=6.0) was interbred, and their progeny were examined. These flies demonstrated a mean training value of 7.5. Calculate realized heritability for olfactory learning in Drosophila.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
20. Quantitative Genetics
Heritability
Problem 18
Textbook Question
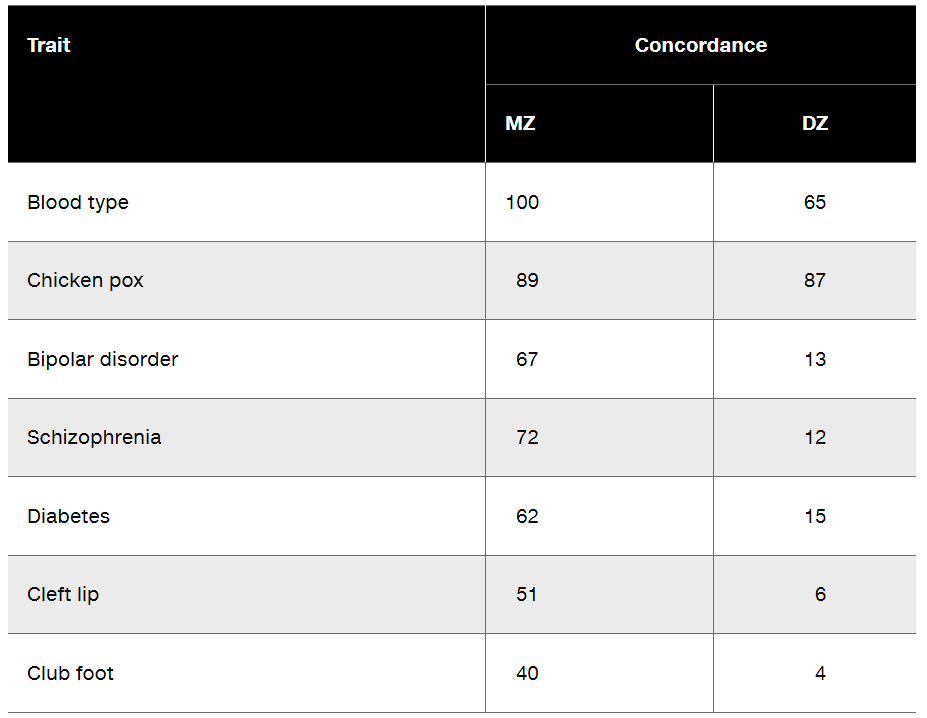
In studies of human MZ and DZ twin pairs of the same sex who are reared together, the following concordance values are identified for various traits. Based on the values shown, describe the relative importance of genes versus the influence of environmental factors for each trait.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of concordance rates. Concordance rates measure the likelihood that both individuals in a twin pair exhibit the same trait. Monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly identical genetic material, while dizygotic (DZ) twins share about 50% of their genetic material. Comparing concordance rates between MZ and DZ twins helps determine the relative influence of genetic versus environmental factors.
Step 2: Analyze the concordance rates for each trait. Traits with high concordance in MZ twins compared to DZ twins suggest a stronger genetic influence. Conversely, traits with similar concordance rates in both MZ and DZ twins suggest a stronger environmental influence.
Step 3: Evaluate each trait individually. For example, blood type shows a concordance of 100% in MZ twins and 65% in DZ twins, indicating a strong genetic basis since blood type is determined entirely by inherited genes. Chicken pox, with concordance rates of 89% in MZ twins and 87% in DZ twins, suggests environmental factors play a larger role, as exposure to the virus is the primary determinant.
Step 4: Consider traits with significant differences in concordance rates between MZ and DZ twins. For example, bipolar disorder (67% MZ, 13% DZ), schizophrenia (72% MZ, 12% DZ), diabetes (62% MZ, 15% DZ), cleft lip (51% MZ, 6% DZ), and club foot (40% MZ, 4% DZ) all show much higher concordance in MZ twins, indicating a strong genetic component. However, environmental factors may still contribute to the development of these traits.
Step 5: Summarize findings. Traits like blood type are almost entirely genetically determined, while traits like chicken pox are primarily influenced by environmental factors. For traits such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, diabetes, cleft lip, and club foot, the data suggest a significant genetic influence, but environmental factors may also play a role in their expression.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Concordance Rates
Concordance rates refer to the likelihood that both twins in a pair exhibit the same trait. In twin studies, higher concordance rates in monozygotic (MZ) twins compared to dizygotic (DZ) twins suggest a stronger genetic influence on the trait. For example, a trait with a 100% concordance in MZ twins indicates a strong genetic component, while lower rates in DZ twins highlight the role of environmental factors.
Recommended video:
Guided course

New Alleles and Migration
Genetic vs. Environmental Influences
The distinction between genetic and environmental influences is crucial in understanding trait development. Genetic influences arise from inherited DNA, while environmental influences stem from external factors such as upbringing, lifestyle, and experiences. Analyzing concordance rates helps determine the relative contributions of these influences, with significant differences between MZ and DZ twins indicating a greater genetic role.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Descriptive Genetics
Twin Study Methodology
Twin studies are a research method used to assess the relative contributions of genetics and environment to various traits. By comparing MZ twins, who share nearly all their genes, with DZ twins, who share about 50%, researchers can infer the heritability of traits. This methodology allows for a clearer understanding of how much of a trait's variation is attributable to genetic factors versus environmental influences.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Twin Studies

 7:04m
7:04mWatch next
Master Calculating Heritability with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
414
views
