Which of the following sex chromosome pairs is caused from nondisjunction?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Sex-Linked Genes
Problem 3
Textbook Question
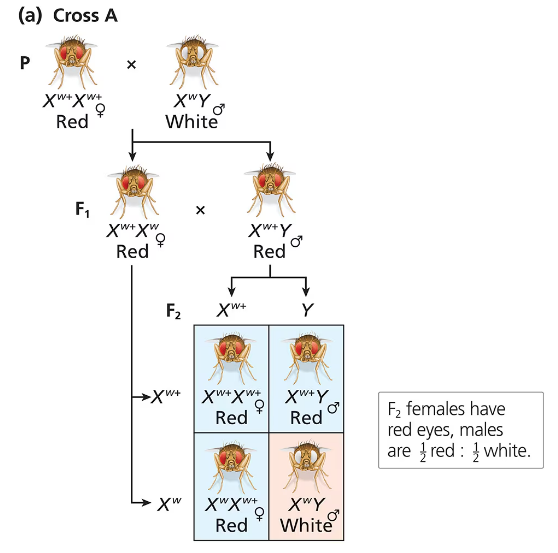
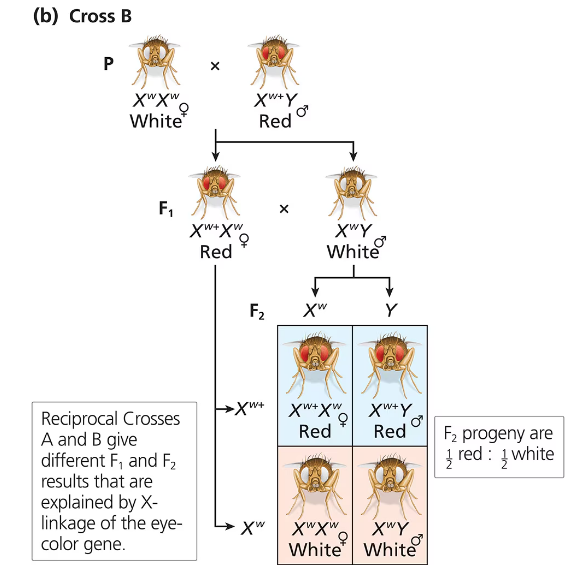
In a test of his chromosome theory of heredity, Morgan crossed a female Drosophila with red eyes to a male with white eyes. The females were produced from Cross A, shown in the Figure below. Predict the offspring Morgan would have expected under his hypothesis that the gene for eye color is on the X chromosome in fruit flies.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the sex chromosomes and eye color alleles involved. In Drosophila, females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The gene for eye color is located on the X chromosome, with red eyes (R) being dominant and white eyes (r) being recessive.
Determine the genotypes of the parents based on the information given. The female has red eyes, so her genotype could be homozygous dominant (XRXR) or heterozygous (XRXr). The male has white eyes, so his genotype must be XrY.
Set up the possible crosses using a Punnett square to predict the genotypes of the offspring. Since the gene is X-linked, consider the inheritance of X chromosomes from the mother and the X or Y chromosome from the father.
Analyze the expected phenotypes of the offspring based on the genotypes. Female offspring receive one X chromosome from each parent, while male offspring receive the X chromosome from the mother and the Y chromosome from the father. Use this to predict eye color in both sexes.
Summarize the expected ratio of red-eyed to white-eyed offspring in males and females according to Morgan's hypothesis that the eye color gene is X-linked.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromosome Theory of Heredity
This theory states that genes are located on chromosomes, which are the carriers of genetic information. It explains how traits are inherited through the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis, linking Mendelian genetics to cytology. Morgan’s work with fruit flies provided key evidence supporting this theory.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Sex-Linked Inheritance
Sex-linked inheritance refers to genes located on sex chromosomes, such as the X chromosome in Drosophila. Traits controlled by these genes show different patterns of inheritance in males and females because males have one X and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sex-Linked Genes
Drosophila Eye Color Genetics
In fruit flies, the gene for eye color is located on the X chromosome. Red eyes are typically dominant over white eyes. When crossing a red-eyed female (XX) with a white-eyed male (XY), the offspring’s eye color depends on the combination of X chromosomes inherited, illustrating sex-linked inheritance.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Morgan's Eye Color Fruit Fly Cross
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
831
views
5
rank


