The following table shows data from a cross examining three genes (a, b, and c). Determine the order of genes
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Trihybrid Cross
Problem 13e
Textbook Question
Researchers cross a corn plant that is pure-breeding for the dominant traits colored aleurone (C1), full kernel (Sh), and waxy endosperm (Wx) to a pure-breeding plant with the recessive traits colorless aleurone (c1), shrunken kernel (sh), and starchy (wx). The resulting F₁ plants were crossed to pure-breeding colorless, shrunken, starchy plants. Counting the kernels from about 30 ears of corn yields the following data.
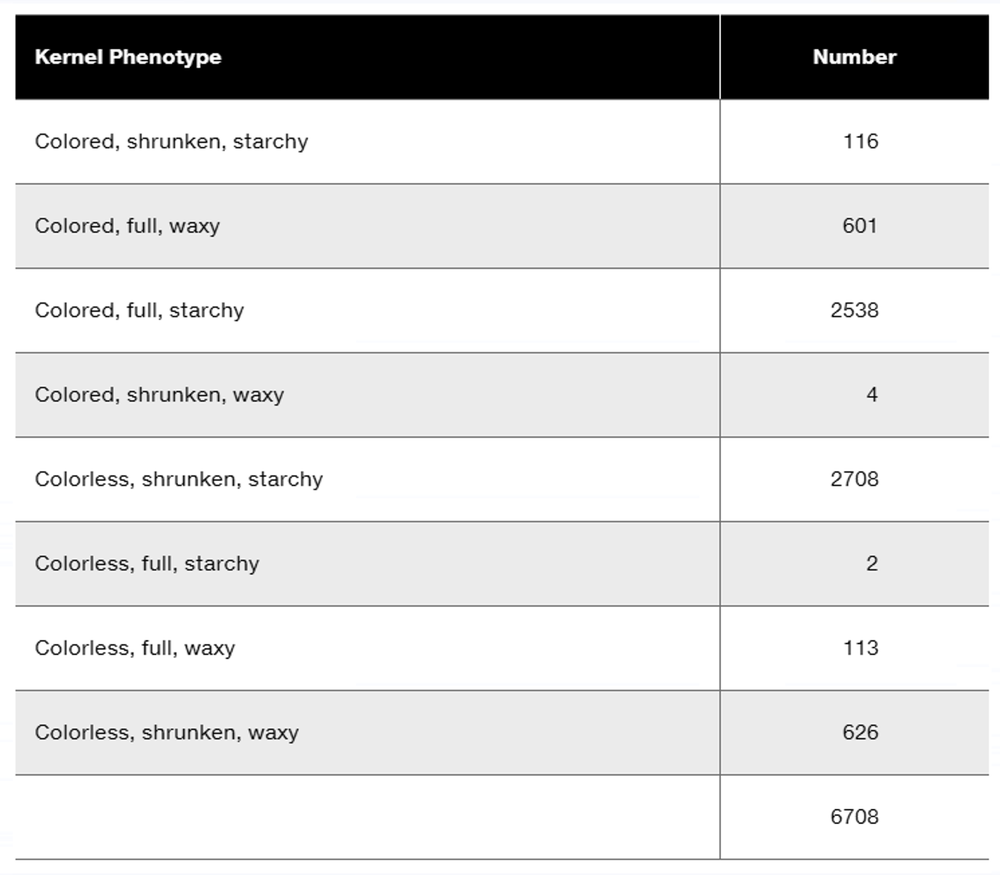
What is the interference value for this data set?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of interference. Interference is a measure of how one crossover event affects the likelihood of another crossover event occurring nearby. It is calculated using the formula: I = 1 - (observed double crossovers / expected double crossovers).
Step 2: Identify the observed double crossovers from the data. In this case, the observed double crossover phenotypes are '+ cu + / se cu e' and 'se + e / se cu e', with numbers 16 and 10 respectively. Add these values to find the total observed double crossovers.
Step 3: Calculate the expected double crossovers. To do this, first determine the recombination frequencies between the genes based on the phenotypic data provided. Multiply the recombination frequencies between the first and second genes and between the second and third genes, then multiply this product by the total number of offspring (6708).
Step 4: Plug the observed and expected double crossover values into the interference formula: I = 1 - (observed double crossovers / expected double crossovers).
Step 5: Interpret the interference value. If the interference value is close to 1, it indicates strong interference (few double crossovers occur). If the value is close to 0, it indicates weak or no interference.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
9mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trihybrid Cross
A trihybrid cross involves the genetic crossing of organisms that differ in three traits, each controlled by different genes. In this scenario, the traits are represented by dominant and recessive alleles, allowing researchers to study inheritance patterns and phenotypic ratios in the offspring. Understanding the principles of Mendelian genetics, including dominance, segregation, and independent assortment, is crucial for analyzing the results of such crosses.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trihybrid Cross
Phenotypic Ratios
Phenotypic ratios represent the relative frequencies of different observable traits in the offspring resulting from a genetic cross. In the context of the question, the phenotypic ratios can be derived from the counts of various kernel types, which help in understanding the inheritance patterns of the traits involved. Analyzing these ratios allows researchers to predict the expected outcomes based on Mendelian principles and assess deviations that may indicate genetic linkage or other factors.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes
Genetic Interference
Genetic interference refers to the phenomenon where the occurrence of one crossover event in a chromosome affects the likelihood of another crossover event occurring nearby. This concept is important when analyzing the results of a trihybrid cross, as it can influence the expected ratios of phenotypes. The interference value can be calculated using observed and expected double crossover frequencies, providing insights into the genetic linkage and the arrangement of genes on chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

RNA Interference
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
548
views
1
rank
2
comments


