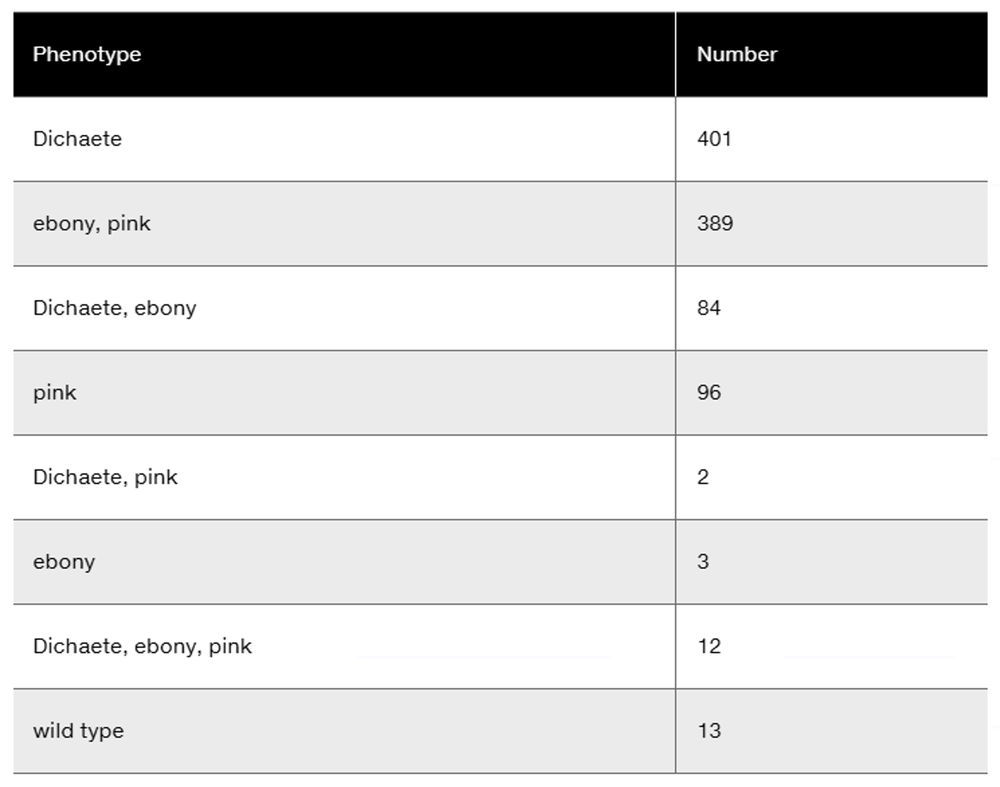
A female of genotype
produces 100 meiotic tetrads. Of these, 68 show no crossover events. Of the remaining 32, 20 show a crossover between a and b, 10 show a crossover between b and c, and 2 show a double crossover between a and b and between b and c. Of the 400 gametes produced, how many of each of the 8 different genotypes will be produced? Assuming the order a–b–c and the allele arrangement previously shown, what is the map distance between these loci?