From a piece of blank paper, cut out three sets of four cigar-shaped structures (a total of 12 structures). These will represent chromatids. Be sure each member of a set of four chromatids has the same length and girth. In set one, label two chromatids 'A' and two chromatids 'a.' Cut each of these chromatids about halfway across near their midpoint and slide the two 'A' chromatids together at the cuts, to form a single set of attached sister chromatids. Do the same for the 'a' chromatids. In the second set of four chromatids, label two 'B' and two 'b.' Cut and slide these together as you did for the first set, joining the 'B' chromatids together and the 'b' chromatids together. Repeat this process for the third set of chromatids, labeling them as 'D' and 'd.' You now have models for three pairs of homologous chromosomes, for a total of six chromosomes. Align the chromosomes as they might appear at metaphase I of meiosis.

Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
Meiotic metaphase I
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Diploid Number

Meiosis

Metaphase I
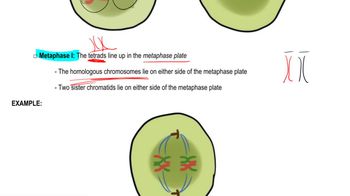
Examine the following diagrams of cells from an organism with diploid number 2n=6, and identify what stage of M phase is represented.
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
End of mitotic telophase
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
End of meiotic anaphase II
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
Early mitotic prophase
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
Mitotic metaphase
