Textbook Question
How is the H+ gradient established?
1251
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

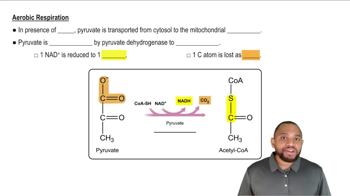
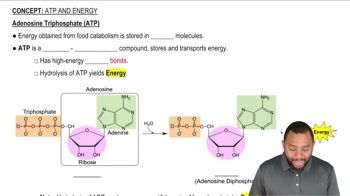
How is the H+ gradient established?
How are glycolysis and the citric acid cycle linked to the production of ATP by electron transport?
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. NADH → NAD+
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. FADH2 → FAD
Caprylic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)6 ― COOH, is a C8 fatty acid found in milk.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of caprylic acid.
Lignoceric acid, CH3 ― (CH2)22 ― COOH, is a C24 fatty acid found in peanut oil in small amounts.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of lignoceric acid.