N-Acetylglucosamine (also known as NAG) is an important component on the surfaces of cells.
b. Draw the structures of the products of acid hydrolysis.

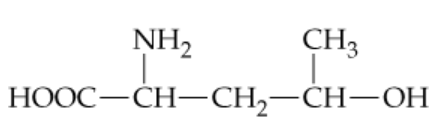
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


N-Acetylglucosamine (also known as NAG) is an important component on the surfaces of cells.
b. Draw the structures of the products of acid hydrolysis.
One phosphorylated form of glycerate is 3-phosphoglycerate
a. Identify the type of linkage between glycerate and phosphate.
Consider the following unnatural amino acid:
a. If two molecules react to form an ester, what is the structure of the ester product?
Draw the structures of the following compounds and use dashed lines to indicate where they form hydrogen bonds to other molecules of the same kind: (ii) methyl formate
Draw the structures of the following compounds and use dashed lines to indicate where they form hydrogen bonds to other molecules of the same kind: (i) formic acid
Arrange these compounds in order of increasing boiling points and explain your rationale for the order.
(i) formic acid
(ii) methyl formate
(iii) formamide.