Textbook Question
What is the ester responsible for the flavor and odor of the following fruit?
b. orange
597
views

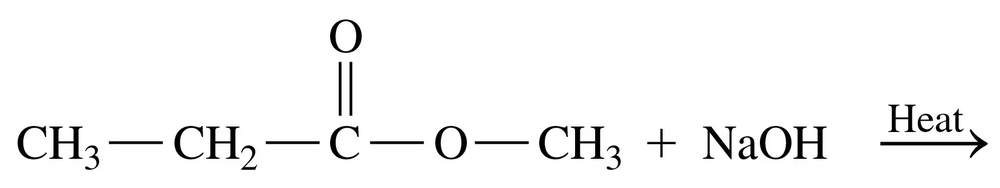
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



What is the ester responsible for the flavor and odor of the following fruit?
b. orange
What is the ester responsible for the flavor and odor of the following fruit?
c. apricot
What are the products of the base hydrolysis of an ester?
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the acid- or base-catalyzed hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the acid- or base-catalyzed hydrolysis of each of the following:
a.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the acid- or base-catalyzed hydrolysis of each of the following:
d.