How do the following interactions help to stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein? Give an example of a pair of amino acids that could give rise to each interaction.
b. Disulfide bonds
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: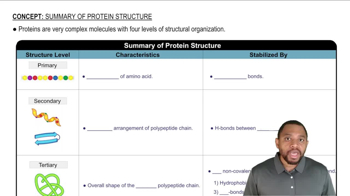



 2:56m
2:56mMaster Summary of Protein Structure Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning