A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
c. How does the primary structure of a protein affect its tertiary structure?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: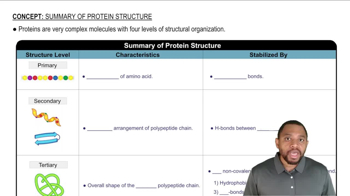


 2:56m
2:56mMaster Summary of Protein Structure Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning