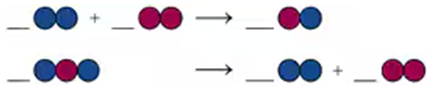
When table sugar (sucrose, C12H22O11) is heated, it decomposes to form C and H2O.
a. Write a balanced equation for the process.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:07m
4:07mMaster Types of Chemical Reactions Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning