Textbook Question
Identify the following features of this phospholipid, which is abundant in the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells:
b. What is the fatty acid?
621
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
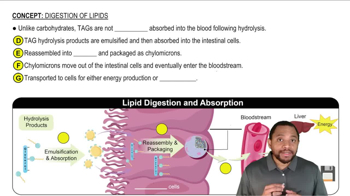
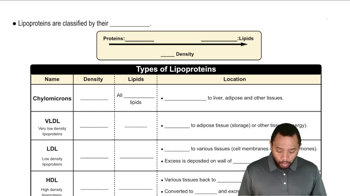

Identify the following features of this phospholipid, which is abundant in the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells:
b. What is the fatty acid?
Identify the following features of this phospholipid, which is needed for the brain and nerve tissues:
a. Is the phospholipid formed from glycerol or sphingosine?
Draw the structure for cholesterol.
Why is LDL called “bad” cholesterol?
Which of the following are steroid hormones?
a. cholesterol
b. cortisol
c. estradiol
d. testosterone
What is the function of the lipid bilayer in a cell membrane?