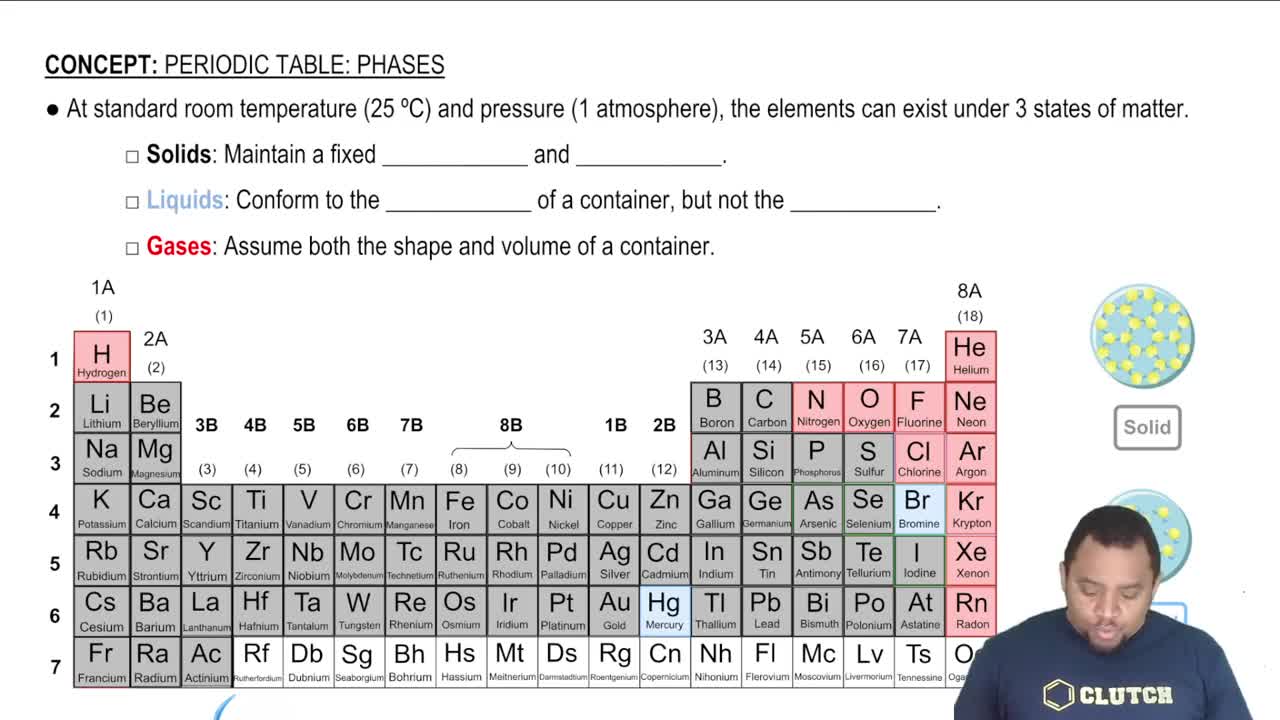
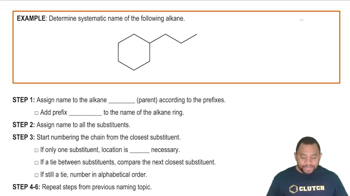
Determine the relationship between each of the pairs of the following compounds. Are they structural isomers (different molecules), conformational isomers (the same molecule), or not related?
(d)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: