Identify the following molecules as an ester, a carboxylic acid, or an amide, and write both the condensed and line-structural formula for each.
a. <IMAGE>
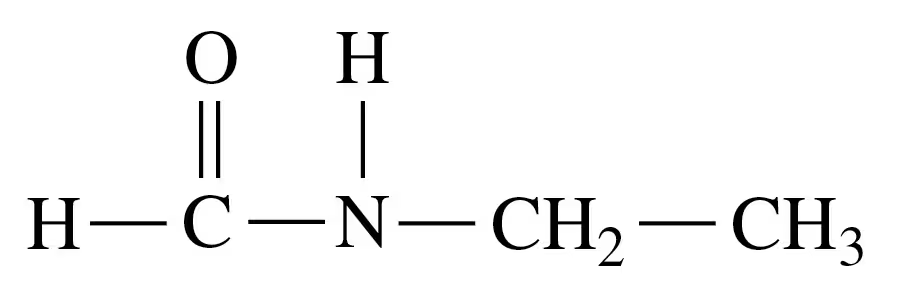
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 :59m
:59mMaster Intro to Amides Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning