Textbook Question
In the following pairs of compounds, which would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why?
a. C8H17COOH or CH3CH2CH2COOH
19
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
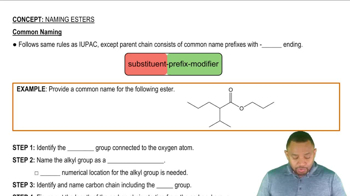


In the following pairs of compounds, which would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why?
a. C8H17COOH or CH3CH2CH2COOH
Write both condensed and line structures for (a) the ester formed when butyric acid reacts with cyclopentanol.
What are the names of the following compounds?
c.
Write the products of the following reactions:
b. 2, 2-Dimethylpentanoic acid + KOH → ?
Write the formulas of potassium salicylate and disodium oxalate.
Draw structures of the amides that can be made from the following reactants:
a. CH3NH2 + (CH3)2CHCOOH →?