Which electronegativity difference (a, b, or c) would you expect for a nonpolar covalent bond?
a. from 0.0 to 0.4
b. from 0.5 to 1.8
c. from 1.9 to 3.3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
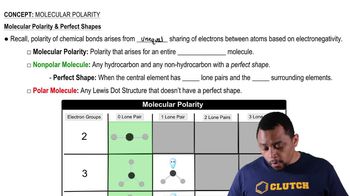
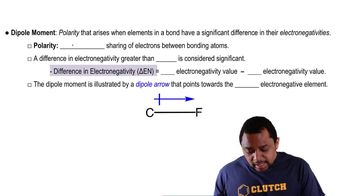

 1:51m
1:51mMaster Dipole Moment (Simplified) Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning