Many biological transformations can be simply classified as additions, eliminations, or substitutions. How would you classify the following reactions?
a. Fumaric acid to malic acid

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
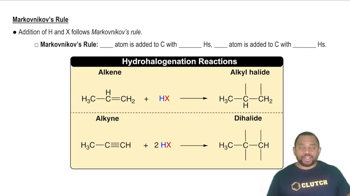
Many biological transformations can be simply classified as additions, eliminations, or substitutions. How would you classify the following reactions?
a. Fumaric acid to malic acid
Many biological transformations can be simply classified as additions, eliminations, or substitutions. How would you classify the following reactions?
b. 2-Phosphoglyceric acid to phosphoenolpyruvic acid
Draw all possible products formed when 2-methyl-2-butene undergoes addition with HCl. Label them as being either the major or the minor product.
Draw the structures of the two different alkenes from which 3-methyl-3-pentanol, shown in the margin, can be made. Draw them in both condensed and line format.
The structure of vinyl acetate is shown below (the partial structure H2C=CH-is known as a vinyl group). When polymerized it produces poly(vinyl acetate), a polymer used for the springy soles in running shoes. Draw the structure of the polymer obtained if three vinyl acetate units underwent polymerization.
Draw structures corresponding to the following names (refer to Table 13.2 if necessary):
a. m-Chloronitrobenzene
b. o-Nitrotoluene
c. p-Methylaniline
d. p-Nitrophenol