Textbook Question
Assume that you have two unlabeled bottles, one with cyclohexane and one with cyclohexene. How could you tell them apart by carrying out chemical reactions?
24
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
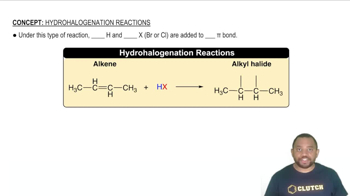


Assume that you have two unlabeled bottles, one with cyclohexane and one with cyclohexene. How could you tell them apart by carrying out chemical reactions?
Cinnamaldehyde, the pleasant-smelling substance found in cinnamon oil, has the following structure:
What products would you expect to obtain from reaction of cinnamaldehyde with water and sulfuric acid catalyst?
Predict the products of the following reactions:
e.
Which of the following compounds are capable of cis–trans isomerism?
a.
b.
c.
Why do you suppose small-ring cycloalkenes like cyclohexene do not exist as cis–trans isomers, whereas large ring cycloalkenes like cyclodecene do show isomerism?