Textbook Question
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
b. Al2X3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: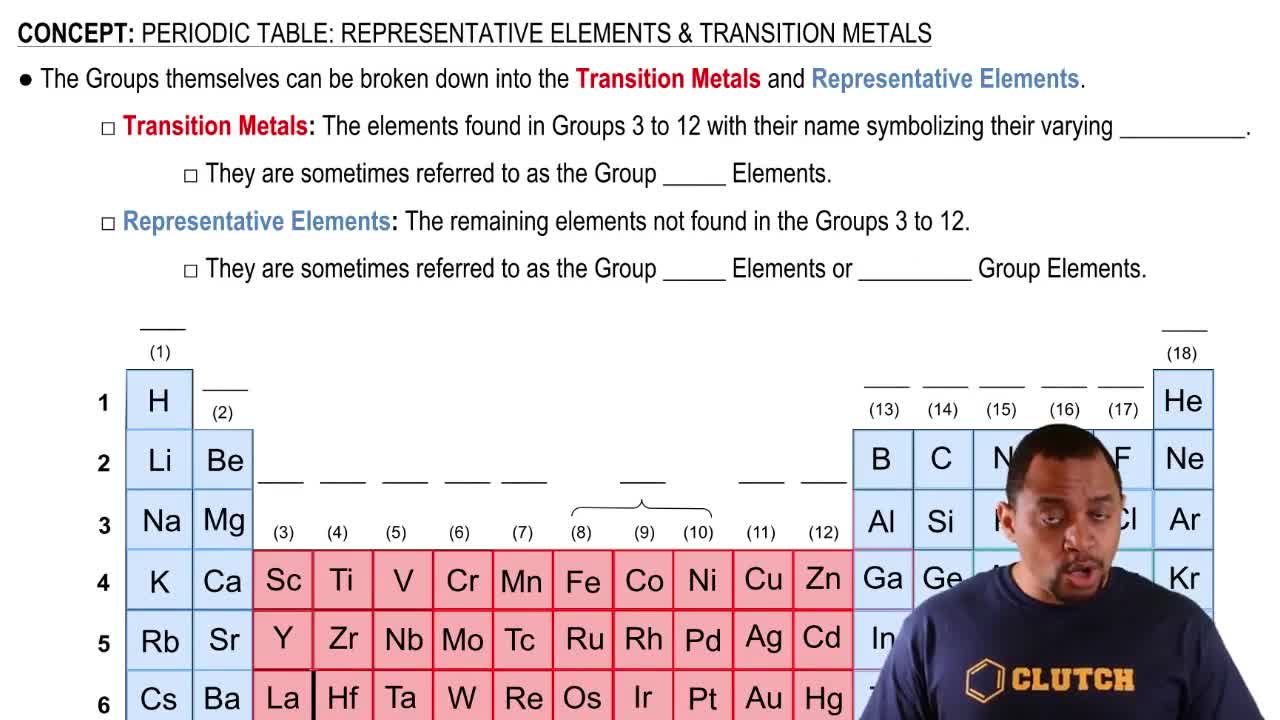



 2:33m
2:33mMaster Ionic Bonding Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning