Epinephrine is the active ingredient in the EpiPen® used to treat severe allergic reactions. EpiPens expire due to the oxidation of the epinephrine. One of these reactions is shown below. Circle the groups in the product that were oxidized.
Ch.5 Chemical Reactions

Frost4th EditionGeneral, Organic and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134988696Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 73b
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(b) 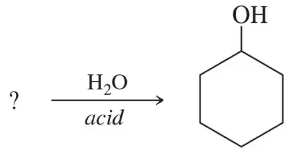
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of hydration reaction. In this case, hydration typically involves the addition of water (H₂O) to an alkene to form an alcohol.
Examine the reactant or product provided in the reaction. If the reactant is an alkene, the product will likely be an alcohol. If the product is an alcohol, the reactant is likely an alkene.
Apply Markovnikov's rule if the reaction involves an unsymmetrical alkene. This rule states that the hydrogen atom from water will add to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms, and the hydroxyl group (OH) will add to the carbon with fewer hydrogen atoms.
Write the structural formula of the missing compound based on the reaction mechanism. Ensure that the correct functional group (e.g., OH for alcohol) is added to the appropriate carbon atom.
Double-check the reaction conditions (e.g., acid catalyst like H₂SO₄) to confirm that the hydration reaction proceeds as expected and that the product or reactant aligns with the given information.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydration Reactions
Hydration reactions involve the addition of water to a compound, typically an alkene, resulting in the formation of alcohols. This process is crucial in organic chemistry as it transforms unsaturated hydrocarbons into more functionalized products. Understanding the mechanism of hydration, including the role of catalysts and the conditions under which these reactions occur, is essential for predicting the products formed.
Recommended video:
Guided course
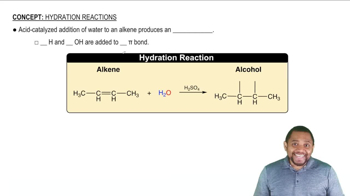
Symmetric Alkene Hydration Concept 1
Markovnikov's Rule
Markovnikov's Rule states that in the addition of HX (where X is a halogen or OH) to an alkene, the hydrogen atom will attach to the carbon with the greater number of hydrogen atoms already attached. This principle helps predict the major product of hydration reactions, guiding chemists in determining the structure of the resulting alcohol. Recognizing this rule is vital for accurately filling in missing reactants or products in hydration equations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
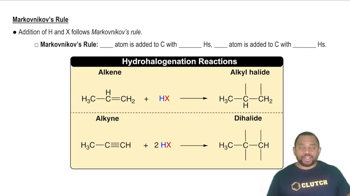
Markovnikov's Rule Concept 2
Reaction Mechanism
A reaction mechanism outlines the step-by-step sequence of elementary reactions that occur during a chemical transformation. In hydration reactions, understanding the mechanism helps in identifying intermediates, such as carbocations, and the role of nucleophiles and electrophiles. This knowledge is crucial for predicting the outcome of the reaction and for understanding how different conditions can affect the product distribution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
590
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the missing organic products for the complete hydrogenation of the following:
(a)
567
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the missing organic products for the complete hydrogenation of the following:
(c)
660
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(a)
676
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(b)
742
views
Textbook Question
How do low-carb diets work? We store glucose molecules in our muscles and liver as glycogen, which consists of thousands of glucose molecules linked together. During periods of fasting, we can activate glycogen to provide glucose.
(a) Determine which of the following reactions below would be a condensation and which would be a hydrolysis.
29
views
