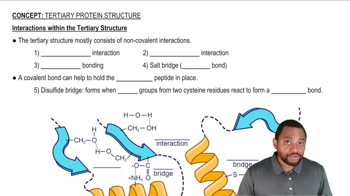
Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. an egg placed in water at 100 °C and boiled for 10 minutes
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: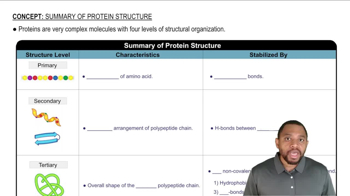


 2:56m
2:56mMaster Summary of Protein Structure Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning