Identify each of the following statements as characteristic of protein denaturation or protein hydrolysis.
a. Milk curdles when lemon juice is added to it.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: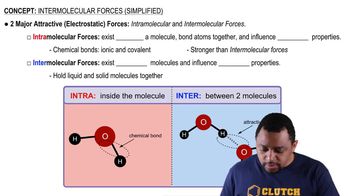
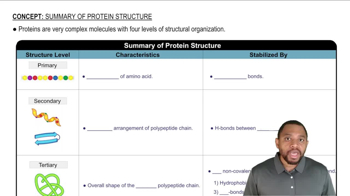


 2:56m
2:56mMaster Summary of Protein Structure Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning