Outline the conditions that direct pyruvate toward the following:
b. Conversion to ethanol and CO2
In what tissues or organisms is each pathway present?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
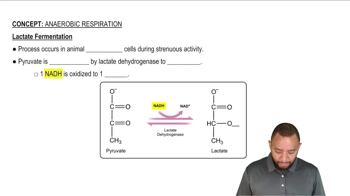


 1:47m
1:47mMaster Anaerobic Respiration Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning