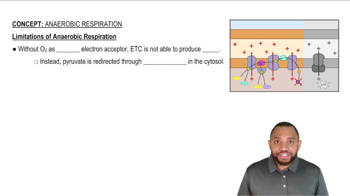
Which of the following conversions would you expect to consume energy and which would you expect to yield energy based on the final oxidation state of the coenzymes involved in each reaction?
a. pyruvate → lactate
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:47m
1:47mMaster Anaerobic Respiration Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning