Textbook Question
Examine the ball-and-stick model of valine below. Identify the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the R group.
<IMAGE>
39
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

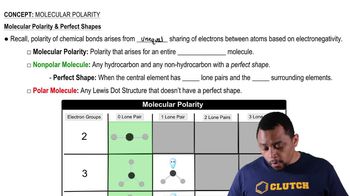
Examine the ball-and-stick model of valine below. Identify the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the R group.
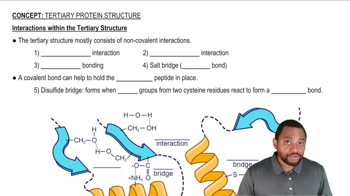
<IMAGE>
Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an α-amino acid or not, and explain why.
a.
Using Table 18.3, name the α-amino acids that (a) contain an aromatic ring, (b) contain sulfur, (c) are alcohols, and (d) have alkyl-group side chains.
Which amino acid is hydrophilic (dissolves in aqueous solutions)? Why?
a. isoleucine
b. phenylalanine
c. aspartic acid
Is serine chiral? Draw serine and identify the chiral atom. Explain why serine is chiral.
Two of the 20 common amino acids have two chiral carbon atoms in their structures. Identify these amino acids and their chiral carbon atoms.