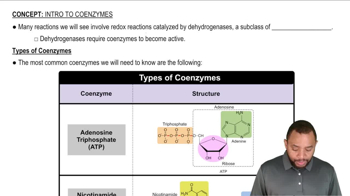
Textbook Question
When pyruvate is used to form acetyl CoA, the product has only two carbon atoms. What happened to the third carbon?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: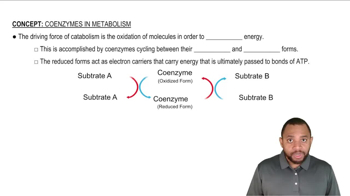

 1:49m
1:49mMaster Pyruvate Oxidation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning