Textbook Question
What coenzymes are needed for the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: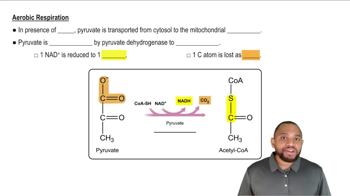


 1:49m
1:49mMaster Pyruvate Oxidation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning